Chapter 296-79 WAC
Last Update: 6/2/20SAFETY STANDARDS FOR PULP, PAPER, AND PAPERBOARD MILLS AND CONVERTERS
WAC Sections
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-010 | Scope and application. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-011 | Definitions. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-020 | General requirements. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-030 | Guards and guarding. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-040 | Fire protection, ignition sources and means of egress. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-050 | Personal protection clothing and equipment. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-070 | Illumination. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-080 | Elevators, manlifts and other lifting devices. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-090 | Electrical equipment and distribution. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-100 | Floors, platforms, stairways, ladders, loading docks. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-110 | Elevated runways and ramps used by vehicles. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-120 | Scaffolds, construction, use and maintenance. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-130 | Crossovers, aisles, passages. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-140 | Installation, inspection, and maintenance of pipes, piping systems, and hoses. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-150 | Powered industrial trucks and other equipment. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-160 | Requirements for cranes and hoists—See general safety and health standards (chapter 296-24 WAC, Part D). |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-170 | Requirements for crawler and truck cranes. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-180 | Privately owned standard gauge railroad operations. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-190 | Loading and unloading materials from railway cars or trucks. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-200 | Bridge and dock plates. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-210 | For conveyors, maintenance and inspection. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-220 | Deactivating and lockout requirements. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-230 | Confined spaces. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-240 | Storage of fuel, oil, flammables and chemicals. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-250 | Safety procedure for handling sulfur. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-260 | Pulpwood storage and handling. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-270 | Pulpwood preparation. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-27003 | Log hauls, slips, and carriages. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-27005 | Band saws. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-27007 | Circular saws speeds and repairs. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-27009 | Slasher saws-tables. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-27011 | Circular swing saws. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-27013 | Drag saws—Fixed chain saws—Circular cut-off saws. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-27015 | Construction and use of pulpwood splitters. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-280 | Chip and hog fuel storage. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-290 | Stock preparation and reprocessing. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29001 | Digester valves and piping. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29003 | Warning of digester being blown. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29005 | Unplugging quick lime stoppages. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29007 | Bleach plant. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29009 | Audible alarm in bleach plant. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29011 | Pocket grinder doors. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29013 | Pulping device procedures. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29015 | Off machine repulping devices. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29017 | Pulping device cleaning, inspection and repairing. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29021 | Shredders and blowers. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29023 | Clearing shredder jams. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29027 | Guillotine type roll splitters. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29029 | Broke hole. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29031 | Industrial kiln guns and ammunition. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29033 | Chlorine dioxide system. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29035 | Piling and unpiling pulp. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-29037 | Chocking rolls. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-300 | Machine room equipment and procedures. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-310 | Converting operations (bag and container manufacturing, printing, coating, finishing and related processes). |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-31001 | General requirements for converting operations (bag and container manufacturing, printing, coating, finishing and related processes). |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-31003 | Corrugator. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-31009 | Die cutting. |
| HTMLPDF | 296-79-320 | Sulfite recovery furnace area requirements. |
DISPOSITION OF SECTIONS FORMERLY CODIFIED IN THIS TITLE
| 296-79-060 | Protection from radiation. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-060, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-060, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
| 296-79-255 | Safety procedure for handling liquid sulfur. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-255, filed 5/6/74.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
| 296-79-27001 | Barkers, chippers, and hog feed devices. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-27001, filed 5/6/74.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
| 296-79-29019 | Guarding hand knives and sharpening steels. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-29019, filed 5/6/74.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
| 296-79-29025 | Repairing shredders. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-29025, filed 5/6/74.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
| 296-79-31005 | Adhesive system. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-31005, filed 5/6/74.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
| 296-79-31007 | Printing and cutting. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-31007, filed 5/6/74.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
| 296-79-31011 | Power lifts on gluers, tapers and stitchers. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-31011, filed 5/6/74.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
| 296-79-31013 | Strapping-banding operations. [Order 74-24, § 296-79-31013, filed 5/6/74.] Repealed by WSR 99-16-083, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. |
PDF296-79-010
Scope and application.
(1) This chapter applies to establishments, firms, persons and corporations that manufacture, process, store, finish, or convert pulp, paper or paperboard and includes all buildings, machinery, and equipment.
(2) This chapter will augment the Washington state general safety and health standards (chapter 296-24 WAC), general occupational health standards (chapter 296-62 WAC), and safety and health core rules (chapter 296-800 WAC). In the event of any conflict between any portion of this chapter and any portion of any of the general application standards, the provisions of this chapter 296-79 WAC, will prevail.
(3) The rules contained in this chapter are minimum requirements and the use of additional guards, or other means, methods or procedures may be needed to make the work or place of work safe.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-010, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, and [49.17].050. WSR 01-11-038, § 296-79-010, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-010, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-010, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-010, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-011
Definitions.
Authorized. A person who is qualified by reason of training and to whom the responsibility to perform a specific assignment has been given by the employer.
Guarded. The means to remove the likelihood of approach or contact by persons or objects to a point of danger.
Hazardous material system. Any system within the following classifications:
(a) Flammable or explosive - Any system containing materials which are hazardous because they are easily ignited and create a fire or explosion hazard, defined by NFPA as Class I liquids;
(b) Chemically active or toxic - Any system containing material which offers corrosion or toxic hazard in itself or can be productive of harmful gases upon release, defined by NFPA 704M as Class 3 and 4 materials;
(c) Thermally hazardous - Any system above 130°F which exposes persons to potential thermal burns;
(d) Pressurized - Any gaseous system above 200 psig or liquid system above 500 psig.
Knowledgeable. The demonstrated ability to communicate the safe work practices required to perform a job or task correctly.
Piping system. Any fixed piping, either rigid pipe or flexible hose, including all fittings and valves, in either permanent or temporary application.
Qualified. A person who is familiar with the construction and operation of the equipment and the duties of the position they may be filling. This includes being aware of the hazards of the job and the means and procedures necessary to eliminate or control those hazards.
Shallor must. As used in this standard means the requirement is compulsory.
Should or may. As used in this standard to identify recommendations or suggestions only.
Training. The procedure that must establish and document the employee's competency in the work practices that they are required to perform.
PDF296-79-020
General requirements.
(1) Housekeeping.
Floors must be kept reasonably clear of spilled or leaking oil, grease, water, broke, etc., that may cause slipping, tripping or falling. Nonskid type surfacing must be installed in vehicular or pedestrian traffic areas where slipping hazards otherwise would exist.
(a) In areas where it is not possible to keep the floor free of materials which cause a slipping hazard, mats, cleats, or other suitable materials which will effectively minimize or eliminate the hazard must be installed.
(b) Hoses, cords, slings or similar items or equipment must be stored in such a manner that they will not create a hazard.
(2) Storage and transportation of materials. Materials, objects or equipment must be stored or transported by methods which will prevent them from falling, tipping or rolling.
(3) Warning of open manholes or excavations must be in accordance with chapter 296-880 WAC, Unified safety standards for fall protection. Open manholes or excavations must be:
(a) Roped off, barricaded, or adequately safeguarded when located in or adjacent to walkways, aisleways, or roadways.
(b) Provided with warning lights or lanterns during periods of darkness or reduced visibility.
(4) Training. Employees must receive proper instruction and be familiar with safe operating procedures:
(a) Before they supervise the operation, or make adjustments to any machine or equipment.
(b) To be able to cope with emergencies arising from breaks, ruptures, or spills which would create a hazardous condition.
(c) For lifting and moving objects. Mechanical devices should be used or employees should ask for assistance in lifting or moving heavy objects.
(d) On prompt reporting of any faulty equipment or hazardous condition to the person in charge.
(5) Working alone. When an employee is assigned to work alone in a remote or isolated area, procedures must be developed to ensure:
(a) That the employee reports by use of radio or telephone to someone periodically; or
(b) That at reasonable intervals a designated person must check on the employee; and
(c) That all persons involved in working alone are advised of the procedures to be followed.
(6) Exits from hazardous areas. Where physically and reasonably possible, there must be at least two unobstructed exits from any hazardous area. Such exits should be on opposite walls.
(7) Safe work area. Sufficient clearance must be maintained between machines to allow employees a safe work area.
(8) Protection from overhead hazard. Warning signs/devices must be:
(a) Placed in conspicuous locations below areas where overhead work is being done; and
(b) Removed promptly when work is completed and the overhead hazard no longer exists.
(9) Welding areas protected.
(a) Areas in which welding is being done must be screened or barricaded to protect persons from flash burns, when practical.
(b) If the welding process cannot be isolated, all persons who may be exposed to the hazard of arc flash must be properly protected.
(10) Testing safety devices. Brakes, back stops, anti-runaway devices, overload releases, emergency stops, and other safety devices must be inspected and tested frequently to ensure that all are operative and maintained in good repair.
(11) Starting and stopping devices.
(a) Electrically or manually operated power starting or stopping devices must be provided within easy reach of the operator from the normal operating position.
(b) If necessary for safety of the operation, the machine must be so equipped that retarding or braking action can be applied at the time of or after the source of power is deactivated.
(12) Interlocks:
(a) Interlocks that affect the safety of employees must not be bypassed except where you demonstrate alternate procedures or devices that provide a level of safety for employees equivalent to those provided by the safety interlock. Interlocks are considered to be bypassed anytime the designed control strategy is bypassed by means including, but not limited to, a temporary wiring change, physical interference or a temporary software change of "force."
(b) Prior to bypassing a safety interlock you must:
(i) Develop a written procedure detailing how the bypass will be accomplished and the alternate means of protecting employees;
(ii) Inform affected employees of all pertinent information including at a minimum the reason for the change, the date of the change, who is responsible for the change, and approximately how long the change will be in effect; and
(c) Post appropriate warning of the change on the equipment or area.
(13) Designing control systems. You must ensure that all control systems are designed to:
(a) Ensure that the system does not create an unsafe state that endangers personnel;
(b) Ensure that when control systems fail, the equipment being controlled fails to a safe state; and
(c) Have an independent method to safely stop the process or equipment, such as a hardwired emergency stop button or other controls that deenergize the system, or independent methods to force the system to a safe state.
(14) Compressed air.
(a) Compressed air must not be used for cleaning clothing that is being worn, or if it will endanger persons in the area.
(b) Sections of high pressure air hoses must be properly coupled and have safety chains or equivalent safety device attached between the sections (30 psi or more is high pressure air).
(15) Punch bars. Open pipes must not be used as punch bars if the use would create a hazard.
(16) Saw table limit stop or extension. Employees must be protected from contact with the front edge of a circular saw by:
(a) A limit stop which will prevent the forward swing of the cutting edge from extending beyond the edge of the table; or
(b) Installation of a table extension.
(17) Powder-actuated tools.
(a) Powder-actuated tool design, construction, operation and use must comply with all requirements specified in "safety requirements for powder actuated fastening systems," (see chapter 296-24 WAC, Part H-1).
(b) A careful check must be made to ensure that no cartridges or charges are left where they could enter equipment or be accidentally discharged in any area where they could create a fire or explosion hazard.
(18) Ladders required on waterfront docks. You must ensure that either permanent ladders or portable ladders:
(a) Are readily available for emergency use on all waterfront docks;
(b) Extend from the face of the dock to the water line at its lowest elevation;
(c) Are installed at intervals not to exceed 400 feet;
(d) Are noticeable by painting the dock area immediately adjacent to the ladder with a bright color which contrasts with the surrounding area; and
(e) Have been secured with a suitable method.
Note: | When working on or around water also see WAC 296-800-160. |
(19) Prevent overhang while removing materials. Extreme care must be taken to prevent material from creating an overhang while removing the materials from piles or bins.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060, and chapter 49.17 RCW. WSR 20-12-091, § 296-79-020, filed 6/2/20, effective 10/1/20. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-020, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, and [49.17].050. WSR 01-11-038, § 296-79-020, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-020, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040 and 49.17.050. WSR 82-13-045 (Order 82-22), § 296-79-020, filed 6/11/82; Order 77-12, § 296-79-020, filed 7/11/77; Order 74-24, § 296-79-020, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-020, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-030
Guards and guarding.
For additional guarding requirements see chapter 296-806 WAC, Machine safety.
(1) Safeguarding specific areas, machines or conditions. Certain equipment, tools, machines, and areas present definite hazards and must be safeguarded by compliance with the following requirements:
(a) Broke shredder cutting heads must be completely enclosed except for opening at feed side sufficient only to permit entry of stock. The enclosure must be:
(i) Bolted or locked in place; and
(ii) Of solid material or with mesh or other openings not exceeding 1/2 inch.
(b) Stitching or sewing machine. Carton or bag stitching machines must be properly safeguarded to prevent persons from coming in contact with the stitching head and other pinch or nip points.
(c) Beaters and pulpers.
(i) A guardrail of standard height must be installed when the top edge of vessels or tubs is less than standard height guardrails above the floor or operator's platform. If necessary for the protection of the person feeding equipment, an intermediate guardrail or other suitable protection shall be installed.
(ii) Beater rolls must be provided with covers.
(d) First dryer. A permanent guard or apron guard, or both, must be installed to protect workers from any exposed ingoing nip of the first dryer drum in each section if the area is accessible to workers while the dryer is in operation.
(e) Floor and drain openings. Floor and drain openings in walkways and general work areas must be covered with material or gratings with openings no larger than 2" in the narrow dimension.
(f) Mechanical devices to dump chip cars, trucks or trailers.
(i) When using mechanical equipment to elevate the front end of the chip containers for dumping into a hopper, the shear area between the floor and the elevated section must be safeguarded.
(ii) The pit area must be adequately safeguarded or barricaded.
(iii) Safeguards must be installed around the exposed sides of a chip hopper.
(2) Replacing guards. All permanent guards must be replaced or adequate temporary safeguards provided before a machine is put into operation.
(3) Protection from moving materials. When material, such as chunks, slivers, cants, or logs, could be thrown or flipped by a saw, barker, or other machines, adequate barricades, screens, netting, or other safeguards must be provided and maintained.
(4) Protection for areas where guards are impractical. When normal guarding is impractical:
(a) The hazard must be reduced to a minimum by use of safety chains, lifelines, signs or other reasonable means; and
(b) Areas which present a hazard which cannot be reasonably safeguarded must be identified by use of paint or other materials.
(5) Knives and scissors.
(a) Knives used for chip or hog fuel machines, or guillotine cutters, must be secured in properly constructed containers during transportation.
(b) Workers must be furnished properly designed and constructed sheaths for safely carrying knives and scissors used for cutting or trimming pulp and paper.
(c) Tables where paper is being cut must be equipped with sheaths or shelves for safe storage of knives and scissors.
(d) Sharp edged slitter knives subject to accidental contact must be effectively guarded. Carriers must be provided and used when transporting or carrying sharp edged slitter knives.
(e) Hand knives and sharpening steels used in paper preparation, must be provided with guards at the junction of the handle and the blade. Utility knives with blade exposure two and one-half inches or less are exempted from this requirement.
(6) Safeguard for foot operated treadle switch used to activate power driven equipment. Foot operated treadle switches used for activation of power driven equipment must be protected by a stirrup type guard or equivalent protection must be provided to prevent accidental activation.
(7) Automatic pressure actuated stopping devices. Hand fed machines and other moving equipment which create shear or pinch points which cannot be reasonably guarded may be safeguarded by the installation of pressure activated bars or sensing devices which, when contacted, will automatically stop the machine or equipment.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-030, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17; WSR 04-14-028, § 296-79-030, filed 6/29/04, effective 1/1/05. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-030, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-030, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-030, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-040
Fire protection, ignition sources and means of egress.
For fire protection, ignition source, and means of egress requirements see chapter 296-24 WAC, Parts G-1 and G-3, WAC 296-800-300 of the safety and health core rules, and chapter 296-811 WAC, Fire brigades.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. WSR 06-01-073, § 296-79-040, filed 12/20/05, effective 3/1/06. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, and [49.17].050. WSR 01-11-038, § 296-79-040, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-040, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-040, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-040, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-050
Personal protection clothing and equipment.
See WAC 296-800-160 for additional personal protective equipment requirements.
(1) Rings or other jewelry that could create a hazard should not be worn by employees while in the performance of their work.
(2) Protective footwear.
(a) Employees who work in areas where there is a possibility of foot injury due to falling or rolling objects must wear safety type footwear.
(b) You will supply shoe guards and toe protectors.
(c) You must also make safety shoes available for purchase by employees at not more than actual cost to you.
(3) Calks or other suitable footwear that will afford reasonable protection from slipping must be:
(a) Worn while working on logs; and
(b) Made available at not more than actual cost to the employer.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-050, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, and [49.17].050. WSR 01-11-038, § 296-79-050, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-050, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: Chapter 49.17 RCW. WSR 94-20-057 (Order 94-16), § 296-79-050, filed 9/30/94, effective 11/20/94; WSR 89-11-035 (Order 89-03), § 296-79-050, filed 5/15/89, effective 6/30/89. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040 and 49.17.050. WSR 83-24-013 (Order 83-34), § 296-79-050, filed 11/30/83; WSR 82-13-045 (Order 82-22), § 296-79-050, filed 6/11/82; Order 74-24, § 296-79-050, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-050, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-070
Illumination.
(1) Illumination required. Lighting that is adequately adjusted to provide a margin of safety for all work tasks must be provided and maintained.
(a) The minimum level of task lighting for all indoor activities must be an average of ten-foot candles measured thirty inches above the floor or at the task.
(b) The minimum level of task lighting for all outdoor activities must be an average of five-foot candles measured thirty inches above the working surface or at the task.
(2) If general lighting is not provided throughout the work area, you must provide illumination which is adequately adjusted to provide visibility of nearby objects that might be potential hazards or to see to operate emergency control or other equipment. The minimum level of nontask lighting for all indoor and outdoor activities must be an average of three-foot candles measured thirty inches above the floor or working surface.
Note: | This section establishes minimal levels of illumination for safety purposes only. Guidelines pertaining to optimal levels of lighting and illumination may be found in practice for Industrial Lighting, ANSI/IES RP7-1979. The minimum levels specified in subsections (1) and (2) of this section represent averages with the lowest level in an area to be no less than fifty percent of the indicated value. |
(3) Emergency or secondary lighting system required.
(a) There must be an emergency or secondary lighting system that can be actuated immediately upon failure of the normal power supply system. The emergency or secondary lighting system must provide illumination in the following areas:
(i) Wherever it is necessary for workers to remain at their machine or station to shut down equipment in case of power failure.
(ii) At stairways and passageways or aisleways used by workers as an emergency exit in case of power failure.
(b) Emergency lighting facilities must be checked at least every 30 days for mechanical defects. Defective equipment must be given priority for repair schedule.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-070, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-070, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-070, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-070, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-080
Elevators, manlifts and other lifting devices.
(1) All elevators, manlifts or other lifting devices must be installed and maintained in conformity with the requirements specified in the Washington state elevator laws and regulations adopted by the elevator section of the department of labor and industries.
(2) Inspection of elevators, etc., for acid towers.
(a) Outside elevators must be inspected daily during winter months when ice materially affects safety.
(b) Elevators, runways, stairs, etc., for acid towers must be inspected monthly for defects that may occur because of exposure to acid or corrosive gases.
(3) Respirators on elevators. Elevators located in areas where exposure to potentially harmful concentrations of toxic substances may occur must be equipped with an adequate supply of respirators to protect the maximum number of passengers.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-080, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-080, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-080, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-090
Electrical equipment and distribution.
All electrical installations and electrical utilization equipment must comply with chapter 296-24 WAC, Part L, and WAC 296-800-280.
(1) Operator controlled devices. Push buttons, selector switches, remote control switches, automatic circuit activating devices, and other control circuit type devices must be marked to indicate their function and the equipment they control.
(2) Posting equipment automatically activated or remotely controlled. If it will create a hazard to personnel, equipment which is automatically activated or remotely controlled must be posted, warning persons that machine may start automatically.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, and [49.17].050. WSR 01-11-038, § 296-79-090, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-090, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: Chapter 49.17 RCW. WSR 91-24-017 (Order 91-07), § 296-79-090, filed 11/22/91, effective 12/24/91; Order 74-24, § 296-79-090, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-090, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-100
Floors, platforms, stairways, ladders, loading docks.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, and [49.17].050. WSR 01-11-038, § 296-79-100, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-100, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-100, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-100, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-110
Elevated runways and ramps used by vehicles.
(1) Runways and ramps must:
(a) Be cleated, grooved, rough surfaced, or covered with a material that will minimize the danger of skidding; and
(b) Not have a maximum incline exceeding 20° from horizontal if used for wheeled equipment.
(2) Guarding exposed sides.
(a) Elevated ramps or runways used for the travel of wheeled equipment must have exposed sides guarded with a substantial bull rail or shear rail of sufficient height to prevent wheeled equipment from going over the rail.
(b) If elevated ramps or runways are used by pedestrians, standard guardrails must be installed on runways wherever the height exceeds 4 feet above the adjacent area in accordance with chapter 296-880 WAC, Unified safety standards for fall protection.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060, and chapter 49.17 RCW. WSR 20-12-091, § 296-79-110, filed 6/2/20, effective 10/1/20. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-110, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-110, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-110, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-110, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-120
Scaffolds, construction, use and maintenance.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, and [49.17].050. WSR 01-11-038, § 296-79-120, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-120, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-120, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-120, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-130
Crossovers, aisles, passages.
See chapter 296-24 WAC, Part D, for additional requirements for aisles and passages.
(1) Clearances to be marked. Low clearance areas under conveyors which could present a hazard to mobile equipment operations must be identified by a suitable means, such as signs, contrasting colors, or tell-tales.
(2) Crossovers over obstructions in passageways. Crossovers must be provided where employees are required to cross over transmission drive lines or other permanent obstructions in passageways or walkways.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-130, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-130, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-130, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-140
Installation, inspection, and maintenance of pipes, piping systems, and hoses.
(1) Design and installation. All new piping systems intended to be used in hazardous material service must be designed and installed in accordance with applicable provisions of the ASME Code for Pressure Piping or in accordance with applicable provisions of ANSI B31.1-1995 through B31.8-1995.
(2) Inspection and maintenance.
(a) You must develop a formal program of installation inspections and maintenance for all hazardous material piping systems. The program must be:
(i) Based on sound maintenance engineering principle;
(ii) Demonstrate due consideration for the manufacturing specifications of the pipe, hose, valves and fittings, the ambient environment of the installation and the corrosive or abrasive effect of the material handled within the system; and
(b) Type and frequency of tests and/or inspections and selection of inspection sites must be adequate to give indications that minimum safe design operating tolerances are maintained. The tests may include visual or nondestructive methods.
(3) Inspection records.
(a) Results of inspections and/or tests must be maintained as a record for each system. Portions of systems that are buried or enclosed in permanent structures in such a manner as to prevent exposure to employees even in the event of a failure, may be exempted from the inspection requirements only.
(i) Past records may be discarded provided the current inspection report and the immediately preceding two reports are maintained.
(ii) When a system is replaced, a new record must be established and all past records may be discarded.
(b) Upon request the records for each system must be made available for review by the department of labor and industries.
(4) Systems or sections of systems found to be below the minimum design criteria requirements for the current service must be repaired or replaced with component parts and methods which equal the requirements for new installations.
(5) Identification of piping systems. USAS A13.1-1956, "Scheme for Identification of Piping Systems," must be followed.
(6) Positive identification of a piping system content:
(a) Must have a lettered legend giving the name of the content in full or abbreviated form, or a commonly used identification system;
(b) Must be made and maintained at suitable intervals and at valves, fittings, and on both sides of walls or floors as needed;
(c) May have arrows to indicate the direction of flow; and
(d) May provide necessary supplementary information, such as hazard of use. This may be done by additional legend or by color applied to the entire piping system or as colored bands. Legends may be placed on colored bands.
(7) Examples of legend which may give both positive identification and supplementary information regarding hazards or use are:
Ammonia . . . . | Hazardous liquid or gas |
Chlorine . . . . | Hazardous liquid or gas |
Chlorine dioxide . . . . | Hazardous liquid or gas |
Sulphur dioxide . . . . | Hazardous gas |
Liquid caustic . . . . | Hazardous liquid |
Liquid sulphur . . . . | Hazardous liquid |
Sulphuric acid . . . . | Hazardous liquid |
Sodium chlorate . . . . | When dry, danger of fire or explosion |
Note: | Manual L-1, published by Chemical Manufacturers Association, Inc., is a valuable guide in respect to supplementary legend. |
(a) When color, applied to the entire piping system or as colored bands, is used to give supplementary information it should conform to the following:
classification | predominant color | |||
F—Fire-protection equipment . . . . | Red | |||
D—Dangerous materials . . . . | Yellow | |||
(or orange) | ||||
S—Safe materials . . . . | Green | |||
(or the achromatic | ||||
colors, white, black, | ||||
gray or aluminum) | ||||
and, when required, | ||||
P—Protective materials . . . . | Bright blue | |||
(b) When legend systems are used, legend boards showing the color and identification scheme in use must be prominently displayed at each plant. They must be located so that employees who may be exposed to hazardous material piping systems will have a frequent reminder of the identification program.
(c) All employees who work in the area of hazardous material piping systems must be given training in the color and identification scheme in use.
(8) Steam hoses. Steam hoses must be specifically designed to safely carry steam at any pressures to which they may be subjected.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-140, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, [49.17].050. WSR 02-12-098, § 296-79-140, filed 6/5/02, effective 8/1/02; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-140, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.050 and 49.17.240. WSR 81-13-053 (Order 81-9), § 296-79-140, filed 6/17/81. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.240, and chapters 43.22 and 42.30 RCW. WSR 81-03-007 (Order 80-31), § 296-79-140, filed 1/8/81; Order 74-24, § 296-79-140, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-140, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-150
Powered industrial trucks and other equipment.
Additional requirements on mobile equipment and lift trucks are in chapter 296-863 WAC.
(1) The operator of a power-driven vehicle must test the brakes, steering gear, lights, horns, warning devices, clutches, etc., before operating vehicle.
(2) Control levers of lift trucks, front end loaders, or similar types of equipment must not be operated except when the operator is in the proper operating position.
(3) No person may be permitted to ride on a powered hand truck unless it is so designed by the manufacturer. A limit switch must be on the operating handle—30 degrees each way from a 45-degree angle up and down.
(4) Employees must not work below the raised bed of a dump truck, raised buckets of front end loaders, raised blades of tractors or in similar positions without blocking the equipment in a manner that will prevent it from falling.
(5) Reporting suspected defects. If, in the opinion of the operator, a power-driven vehicle is unsafe, the operator must report the suspected defect immediately to the person in charge. Any defect that would make the vehicle unsafe to operate under existing conditions will be cause to take the vehicle out of service and it must not be put back into use until it has been made safe.
(6) Vehicle operators must have a reasonably unobstructed view of the direction of travel, or, where this is not possible, the operator must be directed by a person or by a safe guidance means or device. Where practical, mirrors must be installed at blind corners or intersections that will allow operators to observe oncoming traffic.
(7) Vehicles in congested areas must operate with a warning light.
(8) Passengers must not be permitted to ride with legs or arms extending outside any vehicle nor must they be permitted to ride unless a passenger seat or other protective device is provided.
(9) Guard on operator's platform. Every power truck operated from an end platform or standing position must be:
(a) Equipped with a platform extending beyond the operator's position; and
(b) Strong enough to withstand a compression load equal to the weight of the loaded vehicle applied along the longitudinal axis of the truck with the outermost projection of the platform against the flat vertical surface.
(10) Cleaning vehicles. All vehicles must be kept free of excessive accumulations of dust and grease that may present a hazard.
(11) Vehicles must be controlled manually while being pushed or towed except when a tow bar is used. Pushing of vehicles or railroad cars with the forks or clamps of a lift truck is prohibited.
(12) Aisles or passageways should be at least three feet wider than the widest vehicle or load traveling the aisle or passageway. When this clearance cannot be maintained, adequate precautions must be taken.
(13) The forks, clamps, or attachments of lift trucks must be kept as low as possible while the vehicle is moving.
(14) The hoisting of personnel by lift trucks must meet the requirements in WAC 296-863-40060.
(15) Exhaust systems on lift trucks and jitneys shall be constructed to discharge either within 20 inches from the floor or 84 inches or more above the floor.
(16) Mobile equipment with an enclosed cab must be provided with an escape hatch or other method of exit in case the regular exit cannot be used.
(17) Suitable methods must be used or devices installed which will prevent the trailer from tipping while being loaded or unloaded.
(18) Whenever vehicles using LP gas as a fuel are parked overnight or stored for extended periods of time indoors, with the fuel container in place, the service valve of the fuel container must be closed.
(19) The use of spinners on steering wheels must be prohibited unless an anti-kick device is installed or the equipment has a hydraulic steering system.
(20) Rolls transported with a grab or clamp attachment must be carried with the core in a vertical position.
(21) When traveling empty with a grab or clamp attachment, the jaws or blades of those attachments must remain within the running lines of the lift truck.
(22) When transporting two or more rolls with a roll grab attachment, the bottom roll will have at least sixty percent of the grab attachment on it.
(23) When transporting two or more rolls or bales with a grab or clamp attachment, there must be no rolls or bales unsecured if there is risk of part or all of the load shifting or falling.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-150, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-150, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-150, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-150, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-160
Requirements for cranes and hoists—See general safety and health standards (chapter 296-24 WAC, Part D).
Grounding - Where conditions such as corrosive atmospheres, dirt, paint, rust, or other insulating materials prevent reliable metal-to-metal contact for grounding (bridge, wheel and its respective tracks), a separate ground conductor must be provided.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-160, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-160, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-160, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-170
Requirements for crawler and truck cranes.
(1) Boom length indicated. The length must be plainly marked on each boom section of a mobile crane having a sectioned boom.
(2) Radius or boom angle indicator. A radius or boom angle indicator must be installed where it is readily visible to the operator's normal operating position on all cranes having a movable working boom.
(3) Safety device for light fixtures. Any light fixtures attached to a crane boom or machinery house must have a safety strap or other device attached which will prevent the fixture from falling.
(4) Boom stops. Boom stops must be:
(a) Installed to govern the upward travel of the boom to a safe limit; and
(b) Of adequate strength to prevent the boom from traveling past the vertical position.
(5) Controls marked. Crane operating controls must be marked or an explanation of the controls' functions must be posted in full view of the operator.
(6) Locking hydraulic outriggers. Hydraulic outriggers must be:
(a) Equipped with a pilot operated check valve; or
(b) Installed with a mechanical lock which will prevent outriggers from retracting in case of failure of the hydraulic system.
(7) Top of boom painted. The top six feet of the boom or jib must be painted bright yellow or other bright contrasting color if the boom is yellow.
(8) Warning devices. All cranes must be equipped with a suitable warning device such as a horn or whistle.
(9) Hook safety device. All hooks must be equipped with a safety device or other effective means must be used to prevent accidental unhooking of the load.
(10) Counterweight limited. The amount of crane counterweight must not exceed the maximum amount specified by the crane manufacturer.
(11) Use proper size wire rope for sheaves. The size and diameter of sheaves and wire rope must be compatible and follow the recommendations by the manufacturer, published by the Wire Rope Institute or other acceptable engineering practices.
(12) Loading or unloading gear. Unloading gear such as grapples, tongs, and buckets, must not be left suspended when not in use or whenever the machine is unattended.
(13) No one under load. Personnel must not position themselves under crane loads and such loads must not be carried over workers.
(14) Operating clearance from stationary objects. Where the area is accessible to workers:
(a) A distance of 30 inches must be maintained between the outermost part of a revolving crane and any stationary object within the swing radius of the crane; or
(b) The hazardous area must be temporarily guarded or barricaded.
(15) See WAC 296-24-960 when working around energized lines.
(16) Operators must avoid contacting overhead obstructions which may damage the boom or adversely affect stability. In instances where the operator may have difficulty in observing clearances, a signal person must be stationed where they can observe clearances and signal the operator.
(17) Safe travel across thoroughfares or railroad tracks.
(a) When moving cranes, shovels or similar types of equipment across thoroughfares or railroad tracks and the operator does not have a clear vision of approaching traffic, a flag person must be used.
(b) The flag person must be stationed where the equipment operator can be signaled and other traffic can be controlled.
(18) Only a designated member of the crew may give signals to the crane operator. Exception: Anyone may give an emergency stop signal.
(19) Standard hand signals. When using visual signals, standard hand signals as illustrated below, must be used for directing crane operators.
crawler, locomotive, and truck cranes
standard hand signals for cranes
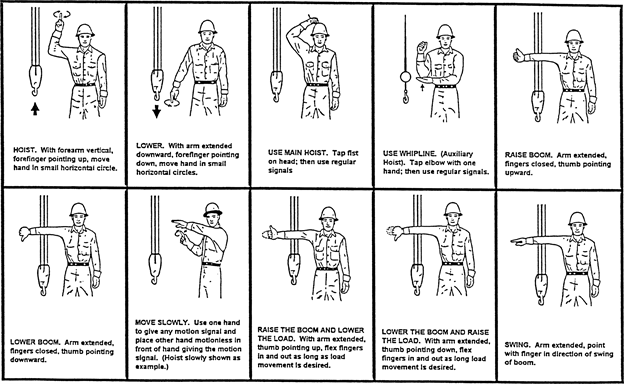 |
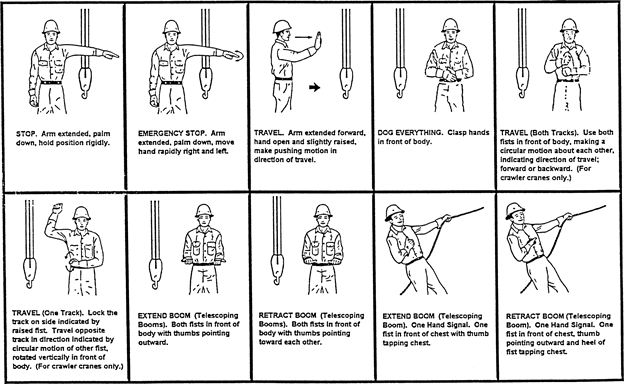 |
standard hand signals for controlling overhead and gantry cranes
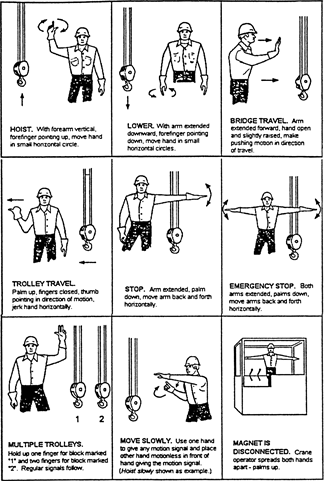 |
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-170, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-170, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.050 and 49.17.240. WSR 81-13-053 (Order 81-9), § 296-79-170, filed 6/17/81. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.240, and chapters 43.22 and 42.30 RCW. WSR 81-03-007 (Order 80-31), § 296-79-170, filed 1/8/81; Order 74-24, § 296-79-170, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-170, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-180
Privately owned standard gauge railroad operations.
(1) Blue flag or light for railroad operations.
(a) A blue signal (blue flag or blue light for nonilluminated areas) must be displayed at one or both ends of an engine, car(s), or train, to indicate that workers are under or about the railway equipment.
(b) When such warning devices are displayed, the equipment must not be coupled to or moved.
(c) On a dead end spur, a blue signal may be displayed adjacent to the switch opening while cars are being loaded or unloaded.
(2) Blue signals and derails.
(a) Work being carried on which subjects employees to the hazard of moving railroad equipment must be protected by blue signals and locked derails set a minimum of 50 feet from one or both ends of the worksite.
(b) Where the spur track switch is less than 50 feet from the work location, the switch padlocked in the open position will take the place of the derail and the blue signal must be placed at that point.
(3) Signals unobscured. Equipment which would obscure the blue signal must not be placed on the track.
(4) Signals displayed by each maintenance crew. Each maintenance crew must display and remove its own set of blue signals.
(5) Warning device.
(a) A flashing warning light or other device must be installed near any opening which leads to a passageway crossing railroad tracks adjacent to the building.
(b) Such light or device must be activated prior to any switching or movement of railroad equipment to warn workers of the dangerous condition in the area.
(6) Cars to be immobilized. Spotted cars must either have brakes set, wheels blocked, or must be coupled to other immobilized cars to prevent each car from rolling.
(7) Crawling under or between coupled cars prohibited. Workers must not crawl under or pass between coupled railroad cars to cross tracks.
(8) Warning at road crossing. An audible whistle, horn or bell must be sounded by the locomotive engineer to give adequate warning prior to switching across any road crossing.
(9) Flying switches. When switching railroad equipment in congested areas or across roadways or walkways "flying switches" must be prohibited.
(10) Car opening devices. All box car doors and associated mechanisms must be carefully inspected before workers attempt to open or close them. If the door is not free and cannot be opened safely by hand, equipment must be provided, where necessary, and a safe method must be used to open or close the door.
(11) Clearance from railroad tracks. Materials must not be stacked or piled closer than 8 1/2' from the center line of a standard gauge railroad track.
(12) Operating under limited visibility conditions.
Unless trains are operated in a manner to allow the operator to see a safe stopping distance in the direction of travel, a flag person(s) must be positioned in such a manner to safely direct movement of the train.
(13) A flag person must:
(a) Remain within sight of the operator; or
(b) Be equipped to maintain visual or voice communication with the operator as conditions dictate.
(14) A flag person must direct the movement of trains being moved across main roads or thoroughfares which do not have adequate traffic warning lights, bells or barricades.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-180, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-180, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.240, and chapters 43.22 and 42.30 RCW. WSR 81-03-007 (Order 80-31), § 296-79-180, filed 1/8/81; Order 74-24, § 296-79-180, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-180, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-190
Loading and unloading materials from railway cars or trucks.
(1) Safe access to top of railroad cars or trucks. Platforms with ladders or stairways must be installed or made available when needed so that workers may safely gain access to and perform work on the top of railroad cars or trucks when ladders are not installed on such equipment.
(2) Nets not to cover ladders. Rolled chip nets must not be positioned where they cover the ladders on railroad cars or trucks.
(3) Tipple type unloading device. When a tipple type unloading device is used for removing chips from cars, the cars must be properly secured in place and all employees must be in the clear before dumping operation is started.
(4) Handling pulp chips and hog fuel from trucks and trailers.
(a) Elevating platform-type or cable-lift type unloading devices must have adequate back bumper stops.
(b) Side rails or other positive means to prevent the trailer from falling must be used while unloading single trailer units.
(c) The truck or tractor must be secured when elevating platform lifts are used to elevate both the tractor and trailer or single unit trucks.
(d) All personnel must be clear of all hoisting or elevating mechanisms before dumping commences.
(e) No person is allowed in any truck while the truck is being elevated.
(5) Taking chip samples. A safe area and suitable device must be provided for the chip tester to use while taking chip samples.
(6) Derail required for hazardous materials. To protect tank cars from being moved while loading or unloading hazardous materials by use of pipes or hoses, a derail and blue flag must be set between the spotted tank cars and any moving railroad equipment.
(7) Moving cars by tugger or powered drums. When rail cars are moved by a tugger or powered drums with cables, a means should be provided or the area barricaded in such a manner that the moving cables do not endanger the workers.
(8) Handling pulpwood from flatcars and all other railway cars.
(a) Railroad flatcars for the conveyance of pulpwood loaded parallel to the length of the car must be equipped with safety-stake pockets.
(b) Where pulpwood is loaded crosswise on a flatcar sufficient stakes of sizes not smaller than 4 by 4 inches must be used to prevent the load from shifting.
(c) Cutting stakes on log bundles. When it is necessary to cut stakes:
(i) Those on the unloading side should be partially cut through first, and then the binder wires cut on the opposite side;
(ii) Wire cutters equipped with long extension handles must be used; and
(iii) No person is permitted along the dumping side of the car after the stakes have been cut.
(d) Cutting bands on log bundles. When cutting bands on bundled logs, workers must:
(i) Position themselves in a safe location;
(ii) Not use double bitted axes for cutting bands;
(iii) Use caution to prevent being struck by ends of bands being cut; and
(iv) If needed, wear personal protective equipment.
(e) Flatcars and all other cars must be:
(i) Chocked during unloading; and
(ii) Rail clamping chocks must be used when equipment is not provided with hand brakes.
(9) Handling pulpwood from trucks.
(a) Cutting of stakes and binder wires must be done in accordance with (8)(c) of this section.
(b) Binders or stakes must not be loosened or removed:
(i) Until the logs are secured and held by equipment which will prevent them from rolling off the truck; or
(ii) Barricades will prevent logs from striking the person removing the binders or stakes.
(c) Where binder chains and crane slings are used:
(i) The crane slings must be attached and taut before the binder chains are released; and
(ii) The hooker must see that the helper is clear before signaling for the movement of the load.
(d) The truck driver must:
(i) Leave the truck cab and remain in the clear, preferably in a designated area; and
(ii) Be in clear view of the unloading equipment operator while the unloader is approaching the loaded truck.
(e) After a complete load is lifted as a unit and held stationary, the truck driver may enter the cab and drive forward from under the suspended load.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-190, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-190, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-190, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-190, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-200
Bridge and dock plates.
Properly constructed bridge or dock plates must be furnished and used to bridge the area between a dock and truck or railroad car. The following requirements must be complied with for construction and use of such bridge or dock plates:
(1) Strength. The plate must be capable of supporting three times the maximum load to which it will be subjected.
(2) Stops. The plates must be provided with positive stops to prevent the plates from shifting or moving.
(3) Plates.
(a) The plates must bear solidly on the dock and on the floor of the car or truck.
(b) Plates with excessive teeter or rock must be repaired or replaced.
(4) Upturn or lip on plates. The sides of bridge or dock plates must have an upturn or lip of at least 4 inches covering the area between the edge of the loading dock and edge of car or truck floor whenever this distance exceeds 18 inches to prevent wheeled equipment from running off the sides.
(5) Bearing surface. Bridge or dock plates must have at least 6 inches bearing surface on the loading dock.
(6) Suitable fittings to be used. Bridge or dock plates intended to be moved by mechanized equipment must be designed for this purpose or appropriate fittings or attachments must be used.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-200, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-200, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-200, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-200, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-210
For conveyors, maintenance and inspection.
See WAC 296-806-420 Conveyors.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-210, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-210, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-210, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-210, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-220
Deactivating and lockout requirements.
(1) Control requirement. Whenever the unexpected startup of machinery, the energizing of electrical circuits, the flow of material in piping systems or the removal of guards would endanger workers, such exposure must be prevented by deactivating and locking out the controls as required by chapter 296-803 WAC, Lockout/tagout (control of hazardous energy).
EXCEPTION: | In instances where any machine must be in motion for proper adjustment, for removal or replacement of materials from the machine, for machine clothing changes or for roping up, the following precautions must be observed. |
(a) The machine must be operated at thread or jog speed;
(b) Extension tools which minimize personnel exposure must be used where possible;
(c) The operating controls must at all times be under the control of a qualified operator or craftsman;
(d) All personnel must remain in view of the operator or other means of communication shall be established; and
(e) All personnel must be beyond the reach of other machine section(s) or element(s) which offer potential exposure. In any instance where such potential exposure exists, such other section(s) or element(s) must be separately locked out.
(2) Group lockout or tagout devices. Procedures must meet the minimum requirements of chapter 296-803 WAC, Lockout/tagout (control of hazardous energy). You must develop a specific written group lockout or tagout procedure and review it with the local plant labor/management safety committee before it can be utilized.
(3) Temporary or alternate power.
(a) Whenever possible, temporary or alternate sources of power to the equipment being worked on must be avoided.
(b) If the use of such power is necessary, all affected employees must be informed and the source of temporary or alternate power must be identified.
(4) Deactivating piping systems.
(a) Nonhazardous systems must be deactivated by at least locking out either the pump or a single valve.
(b) Lockout of the following hazardous material piping systems must isolate to the worksite and must provide protection against backflow where such potential exists:
(i) Gaseous systems that are operated at more than 200 psig;
(ii) Systems containing any liquid at more than 500 psig;
(iii) Systems containing any material at more than 130°F;
(iv) Any cryogenic system;
(v) Systems containing material which is chemically hazardous as defined by NFPA 704 1996 Class 3 and 4; and
(vi) Systems containing material classified as flammable or explosive as defined in NFPA Class I.
(c) Such systems must be deactivated by one of the following:
(i) Locking out both the pump and one valve between the pump and the worksite;
(ii) Locking out two valves between the hazard source and the worksite;
(iii) Installing and locking out a blank flange between the hazard source and worksite. When a blank flange (blind) is used to separate off portions of hazardous material systems from a portion which is in operation, you must develop and implement a procedure for installation and removal of the blank flange that will ensure all hazards have been eliminated;
(iv) Line breaking between the hazard and the worksite;
(v) On hazardous chemical systems where the methods already listed are not feasible, or by themselves create a hazard, single valve closure isolation may be used provided that potentially exposed employees are adequately protected by other means such as personal protective equipment;
(vi) On all steam systems where the methods already listed are not feasible, single valve closure isolation may be used provided that the system is equipped with valves meeting all requirements of ANSI B16.5-1996 and ANSI B16.34-1996. Where single valve isolation is used, the steamline must also be equipped with a bleed valve downstream from the valve closure to prove isolation of the worksite.
Note: | Bleeder valves are recommended behind all primary valve closures on hazardous material systems. Consideration should be given to the nature of the material in the system when installing bleeder valves. To assist in preventing plugging, bleeder valves should generally be installed in the top one-third of the pipe. Short exhaust pipes should be installed on bleeder valves to direct the flow of possible escapement away from the position where an employee would normally be when using the bleeder valve. |
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-220, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17; WSR 04-15-105, § 296-79-220, filed 7/20/04, effective 11/1/04. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-220, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.050 and 49.17.240. WSR 81-13-053 (Order 81-9), § 296-79-220, filed 6/17/81. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.240, and chapters 43.22 and 42.30 RCW. WSR 81-03-007 (Order 80-31), § 296-79-220, filed 1/8/81; Order 76-7, § 296-79-220, filed 3/1/76; Order 74-24, § 296-79-220, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-220, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-230
Confined spaces.
(1) Entry into confined spaces must be in accordance with chapter 296-809 WAC.
(2) All equipment necessary to perform the work, including safety equipment, must be at the confined space and must be inspected or tested to assure that it functions properly.
(3) Protective equipment that will afford proper protection to the employee from any condition which may arise based on the hazard assessment, must be available either at the entrance or within the confined space.
(4) Electrical circuits leading into confined spaces where electrical conductive hazards exist must be protected by a ground fault interrupter or the voltage must not exceed 24 volts.
(5) Battery operated flashlights or lantern must be readily available for use by persons working in areas where escape would be difficult if normal lighting system should fail. Only explosion-proof type lights may be taken into any atmosphere which may contain an explosive concentration.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-230, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-230, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-230, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-230, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-240
Storage of fuel, oil, flammables and chemicals.
See chapter 296-24 WAC, Part E.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-240, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 76-7, § 296-79-240, filed 3/1/76; Order 74-24, § 296-79-240, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-240, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-250
Safety procedure for handling sulfur.
(1) Sulfur burners. Sulfur-burner houses must:
(a) Be safely and adequately ventilated; and
(b) Have every precaution taken to guard against dust, explosion hazards and fires, in accordance with American National Standards Z9.2-1979 (R1991).
(2) Handling/storage of dry sulfur.
(a) Nonsparking tools and equipment must be used in handling dry sulfur.
(b) Sulfur storage bins must be kept free of sulfur dust accumulation, and buildings should be designed with explosion relief, in accordance with the latest revision of American National Standard Z9.2-1979 (R1991).
(c) Sulfur-melting equipment must not be located in the burner room.
(3) Handling/storage of liquid sulfur.
(a) Each facility utilizing liquid sulfur must:
(i) Carefully examine its own handling system; and
(ii) Formulate a written procedure for maintenance, receiving, storing and using this product.
(b) A minimum of two trained employees must be assigned when a tank car is first opened in preparation for venting and unloading.
(c) Approved respiratory protective equipment for H2S exposure, chemical splash goggles and gloves must be worn when performing this work.
(d) Spark producing or electric operated tools must not be used to unplug railroad car vents.
(e) Where venting can cause harmful exposure to other unprotected workers in the area:
(i) A venting system must be installed which adequately contains any gas escapement from a tank car while venting;
(ii) The vented gas must be carried to a safe location for discharge or circulated through a scrubbing system;
(iii) The venting system must be connected before valves which would allow escapement are opened.
(f) Smoking, open burning or welding must be prohibited while unloading is in process or danger of gas escapement exists.
(4) Acid plant - Protection for employees.
(a) Where lime slaking takes place, employees must be provided with rubber boots, rubber gloves, protective aprons, and eye protection. A deluge shower and eyewash must be provided to flush the skin and eyes to counteract lime and acid burns.
(b) Hoops for acid storage tanks must be:
(i) Made of round rods rather than flat strips; and
(ii) Regularly inspected and safety maintained.
(c) Sulphur burner ignitors must have a means to automatically shut off the fuel to the ignitor when the flame has been extinguished.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-250, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-250, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: Chapter 49.17 RCW. WSR 91-24-017 (Order 91-07), § 296-79-250, filed 11/22/91, effective 12/24/91; Order 76-7, § 296-79-250, filed 3/1/76; Order 74-24, § 296-79-250, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-250, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-260
Pulpwood storage and handling.
(1) Piling of logs.
(a) Logs must be piled or removed in an orderly manner;
(b) The piles must be stable and individual logs properly placed to prevent them from rolling or falling;
(c) The ends must not project into walkways, roadways or areas reserved for other purposes; and
(d) Sufficient clearance must be maintained for safe travel of all vehicles and loads.
(2) Wire rope doglines used for towing or rafting must not be used when:
(a) They acquire jaggers to the extent that they present a hazard to the employees handling them; or
(b) They are weakened to the extent that they are hazardous.
(3) Boom sticks must be capable of safely supporting the weight imposed upon them.
(4) Stiff booms must be:
(a) Made by fastening not less than two boom sticks together;
(b) Not less than 36 inches in width measured from outside to outside of the outer logs; and
(c) Fastened together with not less than 4 inch by 6 inch cross ties or cable lashing properly recessed into notches in the boom sticks and secured.
(5) Pike poles must be kept in good repair. Conductive pike poles must not be used when it is possible that they may come in contact with electrical conductors.
(6) Logs must not be lifted over employees and employees must stay clear of the hazardous area near where logs are being lifted or swung.
(7) Storing or sorting on water or any boom work other than boom boat operations, must require a minimum of two persons.
(8) All mobile equipment used to handle logs, blocks or cants must be provided with adequate overhead protection.
(9) Unloading lines must be so arranged that it is not necessary for the worker to attach them on the pond or dump side of the load.
(10) Unauthorized vehicles and unauthorized foot traffic must not be allowed in any active sorting, storing, loading, or unloading areas.
(11) Log unloaders must not be moved about the premises with loads raised higher than absolutely necessary.
(12) Jackets or vests of fluorescent or other high visibility material must be worn by persons working on dry land log storage.
(13) All log dumps must be periodically cleared of bark and other debris.
(14) Handles of wood hooks must be locked to the shank to prevent them from rotating.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-260, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-260, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-260, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-260, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-270
Pulpwood preparation.
(1) Barker feeding devices must be designed in such a manner that the operator will not be required to hold or make any physical contact with any log or bolt during the barking operations.
(2) A dog or locking device in addition to the motor switch, clutch, belt shifter or other power disconnecting device must be installed on all intermittent barking drums to prevent the drum from moving while it is being filled or emptied.
(3) Hydraulic barkers.
(a) The inlet and outlet areas of hydraulic barkers must be equipped with baffles or devices that will reasonably prevent material from flying out while the machine is in operation.
(b) The operator must be protected by at least five-ply laminated glass or material of equivalent strength.
(4) The high pressure hoses of hydraulic barkers must be secured in such a manner that the hose connection ends will be restrained if a hose connection fails.
(5) The feed operator's station must not be in direct line with the chipper blades. Suitable safeguards must be installed to prevent chips or chunks from being thrown out and striking the person feeding the machine.
(6) When the operator cannot readily observe the material being fed into the chipper, a mirror or other device must be installed in such a position that the ingoing material can be monitored.
(7) Metal bars or other nonchippable devices must not be used to clear jams or plug-up at the feed entrance to a chipper or hog while the machine is running.
(8) Water wheel speed governor.
(a) Water wheels, when directly connected to marker disks or grinders, must be provided with speed governors, if operated with gate wide open; and
(b) Water wheels directly connected to pulp grinders must be provided with speed governors limiting the peripheral speed of the grinder to that recommended by the manufacturer.
(9) Knot cleaners of the woodpecker type.
(a) The operators of knot cleaners of the woodpecker type must wear eye protection equipment; and
(b) Such knot cleaners should be enclosed to protect passersby from flying chips.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-270, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-270, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-270, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-270, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-27003
Log hauls, slips, and carriages.
(1) Controls must be:
(a) Arranged to operate from a position where the operator will at all times be in the clear of logs, machinery, lines, and rigging; and
(b) Marked to indicate their function.
(2) Log decks must be provided with effective means to prevent logs from accidentally rolling down the deck and onto the carriage or its runway.
(3) When needed for protection of personnel, an automatic stop or interlocking device must be installed on log hauls or slips. These devices are not a substitute for lockout.
(4) A barricade or other positive stop of adequate strength must be provided to protect the sawyer from rolling logs.
(5) Canting gear or other equipment must not hang over the log deck in such a manner as to endanger employees.
(6) The sawyer must be primarily responsible for the safety of the carriage crew and offbearers and must exercise due care in the operation of the carriage and log turning devices.
(7) Feed works and log turning control levers must be so arranged that they may be secured when not in use and must be adequately guarded against accidental activation.
(8) A control device must be provided so that the sawyer may stop the head rig section of the mill without leaving the stand.
(9) An effective method of disengaging the head rig saws from the power unit must be installed on all head rigs where the power unit is not directly controlled by the sawyer.
(10) The sawyer must be safeguarded either by location or by use of substantial screens or approved safety glass.
(11) Carriages upon which employees are required to work must be solidly decked over and the employees properly protected.
(12) The feed control lever of friction or belt-driven carriage feed works must be designed to operate away from the saws or carriage track.
(13) A substantial stop or bumper must be installed at each end of the carriage run.
(14) Substantial sweeps must be installed in front of each carriage wheel. Such sweeps must extend to within 1/4 inch of the rails.
(15) Where power-operated log turners are used, carriage knees must be provided with goosenecks or other substantial means of protecting the carriage crew.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-27003, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-27003, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-27003, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-27005
Band saws.
(1) Band saws must be given a thorough daily inspection and any deficiency reported and corrected.
(2) Any band saw found to have developed a crack greater than one-tenth the width of the saw must:
(a) Be removed from service until the width of the saw is reduced to eliminate the crack;
(b) Have the cracked section removed; or
(c) Have the development of the crack arrested by welding.
(3) Band saws must not be continued in use on the head rig for which they have been designed after they have been reduced 40% in width.
(4) Band saw guides must be maintained in good condition and proper alignment at all times.
(5) All head band saw wheels must have a minimum rim thickness of 5/8 inches, except for a distance not to exceed one inch from the front edge of the wheel.
(6) Band saws must not be run at a speed in excess of the manufacturer's recommendations.
(7) A band wheel that has developed a crack in the rim must be immediately removed from service. If a crack has developed in a spoke, the wheel must be removed from service until properly repaired.
(8) All band wheel guards must be constructed of not lighter than ten U.S. Gauge metal, or not less than two-inch wood material or equivalent, attached to substantial frames. Necessary ventilating ports, not larger than two by four inches, and suitable doors or gates for the lubrication and repair of the saw will be permitted.
(9) Every band mill must be equipped with a saw catcher, rest or guard of substantial construction.
(10) Each gang ripper of band or straight saw type must have the cutting edges of the saw guarded by a hood or screen substantially secured to the framework of the machine.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-27005, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-27005, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-27005, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-27007
Circular saws speeds and repairs.
(1) Circular saws must not be operated at speeds in excess of those specified by the manufacturers.
(2) Circular saws must be inspected for cracks each time the teeth are filed or set. They must be discontinued from use until properly repaired when found to have developed a crack exceeding the safe limits specified by the manufacturer.
(3) Damaged saws must be repaired only by persons experienced and knowledgeable in this type of work or by a manufacturers representative.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-27007, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-27007, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-27009
Slasher saws-tables.
(1) Slasher saws must be guarded in accordance with WAC 296-79-030(3) of this chapter.
(2) Saws must be stopped and locked or tagged out whenever it is necessary for any person to be on the slasher table.
(3) Saws below table where not protected by the frame of the machine, the underside of the slasher saws must be adequately guarded.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-27009, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-27009, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-27011
Circular swing saws.
(1) Each circular swing saw must be provided with a hood guard that completely encloses the upper half of the saw.
(2) Each swing saw must be equipped with a positive stop at the extent of the swing necessary to cut the material.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-27011, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-27011, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-27013
Drag saws—Fixed chain saws—Circular cut-off saws.
(1) Saws must be so arranged that they will not project into any passageway when in an idle or working position. When existing conditions do not leave clear passage the saws must be fenced off in order to make it impossible for anyone to walk into them.
(2) Log decks must be equipped with a device to hold the material stable when being cut.
(3) Drag saws and fixed chain saws must be equipped with a device that will safely lock them in an "up" position.
(4) All persons must be in the clear before starting operations.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-27013, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-27013, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-27015
Construction and use of pulpwood splitters.
(1) The activating control unit for a splitter must be of the clutch or positive acting type and must be so arranged and designed that it will not repeat without additional activation before starting a second cycle.
(2) The base or rest upon which the wood sits while being split must have a corrugated surface or other means must be provided which will prevent the wood block or log from shifting as the pressure is applied.
(3) The splitter base or rest and wood to be split must be free of ice, snow, and chips.
(4) The splitter machine operator must have a clear, unobstructed view of the work area adjacent to the splitting operation when other workers must be in such area while blocks are being split.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-27015, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-27015, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-27015, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-280
Chip and hog fuel storage.
(1) Entry into chip bins and silos must be in compliance with the requirements of confined space entry, WAC 296-79-230, of this chapter.
(a) Chip and sawdust bins. Steam or compressed air lances, or other safe methods, must be used for breaking bridges and hangups.
(b) Employees must be prohibited from working under or on top overhangs or bridges. Extreme care must be taken to prevent chips or hog fuel from creating an overhang or bridging.
(c) Hog fuel bins must be provided with an approved railed platform or walkways near the top or other approved means must be provided for use of employees engaged in dislodging hog fuel.
(2) Exterior chip and hog fuel storage.
(a) When mobile equipment is used on top of hog fuel or chip piles, a roll-over protection system must be installed on the equipment.
(b) If the cab is of the enclosed type, windshield wipers must be installed.
(c) If used during hours of darkness the area must be adequately illuminated or the equipment must have adequate lights to provide the operator sufficient illumination to safely perform the work.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-280, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-280, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-280, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-280, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-290
Stock preparation and reprocessing.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-290, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-290, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-290, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-29001
Digester valves and piping.
(1) The blow valve of a digester must be arranged so as to be operated from another room, remote from safety valves.
(2) Heavy duty pipe, valves, and fittings must be used between the digester and blow pit, blowtanks and dumptanks. These valves, fittings, and pipes must be inspected at least semiannually to determine the degree of deterioration and should be replaced when necessary.
(3) Digester blow valves or controls must be pinned or locked in closed position throughout the entire cooking period.
(4) Test holes in blow lines of piping systems must not be covered with insulation or other materials.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29001, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29001, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29003
Warning of digester being blown.
(1) Procedures must be developed to ensure that digester operators are aware of personnel entering hazardous areas.
(a) Audible warning signals and red warning lights must be installed in areas which may be hazardous to personnel while digesters are being blown.
(b) Such devices must be activated prior to blowing a digester and the warning lights must remain lighted as long as the hazard exists.
(2) Blowing digester. Blow-off valves must be opened slowly.
(3) After the digester has started to be blown, the blow-off valve must be left open, and the hand plate must not be removed until the person responsible signals the blow-pit person that the blow is completed. Whenever it becomes necessary to remove the hand plate to clear stock, operators must wear eye protection equipment and protective clothing to guard against burns from hot stock.
(4) Blow-pit hoops must be maintained in a safe condition.
(5) Where the processes of the sulfate and soda operations are similar to those of the sulfite processes, the standard of WAC 296-79-29001 and 296-79-29003, of this chapter, applies to both processes.
(6) Means must be provided so the digester cook can signal the employee in the chip bin before starting to load the digester.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-29003, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29003, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 77-12, § 296-79-29003, filed 7/11/77; Order 76-7, § 296-79-29003, filed 3/1/76; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29003, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29005
Unplugging quick lime stoppages.
Water must not be used to unplug quick lime stops or plugs in pipes or confined spaces.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29005, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29005, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29007
Bleach plant.
(1) Work areas used for preparation and processing of bleaching mixtures must be equipped with properly designed exhaust ventilation systems capable of clearing the area of toxic gases. See chapters 296-62 and 296-841 WAC.
(2) Bleaching containers, such as cells, towers, etc., except the Bellmer type, must be completely covered on the top, with the exception of one small opening large enough to allow filling but too small to admit a person.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060. WSR 05-20-055, § 296-79-29007, filed 10/3/05, effective 12/1/05; WSR 05-03-093, § 296-79-29007, filed 1/18/05, effective 3/1/05. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29007, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29007, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29009
Audible alarm in bleach plant.
An audible alarm system must be installed and it must be activated whenever a serious leak or break develops in the bleach plant area which creates a health or fire hazard.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29009, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29009, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29011
Pocket grinder doors.
Doors of pocket grinders must be so designed and arranged as to keep them from closing accidentally.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29011, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29011, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29013
Pulping device procedures.
Each company must develop a safe procedure which must be followed for feeding, clearing jams, or removing foreign objects from any pulping device. These procedures must comply with applicable provisions of this standard.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-29013, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29013, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29013, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29015
Off machine repulping devices.
(1) When fed manually from the floor above, conveniently located emergency stop devices must be provided at the top level.
(2) When fed from floor above:
(a) The chute opening, if less than standard guardrail height from the feed platform or floor, must be provided with a complete guardrail or other enclosure to standard guardrail height; and
(b) Openings for manual feeding must be sufficient only for entry of stock and must be provided with at least two permanently secured crossrails, in accordance with, the general safety and health standards, WAC 296-24-75003.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-29015, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29015, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29015, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29017
Pulping device cleaning, inspection and repairing.
When cleaning, inspecting or performing other work that requires that persons enter pulping devices, all control devices must be locked or tagged out in accordance with the requirements of this standard.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29017, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29017, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29021
Shredders and blowers.
(1) On manually fed broke shredders, the feed table must be of a height and distance from the knives as to prevent the operator from reaching or falling into the knives or the operator must be safeguarded by other acceptable means.
(2) A smooth-pivoted idler roll resting on the stock or feed table must be provided in front of feed rolls except when arrangements prevent the operator from standing closer than 36 inches to any part of the feed rolls.
(3) Any manually fed cutter, shredder, or duster must be provided with an idler roll as specified in (2) of this section or the operator must use special hand-feeding tools.
(4) Blowers used for transporting materials must be provided with feed hoppers having outer edges located not less than 48 inches from the fan.
(5) The blower discharge outlets and work areas must be arranged to prevent material from falling on workers.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-29021, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29021, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29021, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29023
Clearing shredder jams.
To clear jams or blockage to the machine, the operator must use objects which will not create a hazard. The use of metal bars for such purposes is prohibited.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29023, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29023, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29027
Guillotine type roll splitters.
(1) The engaging control for activating the guillotine blade must be a "deadman type" switch that demands continuous operator activation and must be:
(a) A positive two-hand operating control; or
(b) Located far enough from the cutting location so that the operator cannot reach the blade during the cutting process.
(2) Personnel must not position any part of the body under the blade.
(3) Rolls must be in the horizontal position while being split.
(4) Rolls must be centered directly below the blade.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-29027, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29027, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 76-7, § 296-79-29027, filed 3/1/76; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29027, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29029
Broke hole.
(1) An alarm bell or flashing light must be actuated or other suitable warning must be given before dropping material through a broke hole when persons working below may be endangered.
(2) Broke holes must be guarded to the fullest extent possible consistent with operational necessities. The degree of guarding provided by standard height and strength guardrails will be considered as a minimum acceptable level of protection.
(3) When repulping devices or feed conveyor systems for repulping devices are located beneath broke holes, special precautions must be used:
(a) The broke hole opening must be reduced to the smallest practical dimension;
(b) If the broke hole opening is large enough to permit a worker to fall through and is not guarded at least to the equivalent degree of protection provided by standard guardrails, any employee pushing broke down the broke hole must wear a safety belt or harness attached to a lanyard; and
(c) The lanyard must be fastened in such a manner that it is impossible for the person to fall into the repulping device.
(4) Guarding to the equivalent degree of protection provided by standard guardrails and meeting the requirements of subsections (2) and (3), may be achieved by the use of guard bars separated no more than 15-1/2 inches in a vertical plane and 12 inches in a horizontal plane, or any other location within that segment.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-29029, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29029, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.240, and chapters 43.22 and 42.30 RCW. WSR 81-03-007 (Order 80-31), § 296-79-29029, filed 1/8/81; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29029, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29031
Industrial kiln guns and ammunition.
You must ensure that there are written instructions, including safety procedures, for storing and operating industrial kiln guns and ammunition. All personnel working with this equipment must be instructed in these procedures and must follow them.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-29031, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29031, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29031, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29033
Chlorine dioxide system.
(1) Sodium chlorate.
(a) Personnel handling and working with sodium chlorate must be thoroughly instructed in precautions to be used in handling and special work habits.
(b) Facilities for storage and handling of sodium chlorate must be constructed so as to eliminate possible contact of dry or evaporated sodium chlorate with wood or other material which could cause a fire or explosion.
(c) Sodium chlorate facilities should be constructed with a minimum of packing glands, stuffing boxes, etc.
(2) Chlorine dioxide.
Chlorine dioxide generating and storage facilities must be placed in areas which are adequately ventilated and are easily kept clean of wood, paper, pulp, etc., to avoid contamination which might cause a reaction. This can be accomplished by placing these facilities in a separate room or in a designated outside space.
(3) General.
(a) Facilities handling sodium chlorate and chlorine dioxide must be declared "no smoking" areas and must have signs posted accordingly.
(b) Management must be responsible for developing written instructions including safety procedures for operating and maintaining the generator and associated equipment. All personnel working on this equipment must be thoroughly trained in these procedures and must follow them. A periodic review of these procedures is recommended.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-29033, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29033, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29033, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29035
Piling and unpiling pulp.
(1) Piles of wet lap pulp (unless palletized) must be stepped back one-half the width of the sheet for each 8 feet of pile height. Sheets of pulp must be interlapped to make the pile secure. Pulp must not be piled over pipelines to jeopardize pipes, or so as to cause overloading of floors, or to within 18 inches below sprinkler heads.
(2) Piles of pulp must not be undermined when being unpiled.
(3) Floor capacities must be clearly marked on all floors.
(4) When sprinklers are used for fire protection in the storage area, baled paper and rags must be stored in stable piles which do not extend into the area necessary for the proper function of sprinkler systems.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29035, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 76-7, § 296-79-29035, filed 3/1/76; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29035, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-29037
Chocking rolls.
Rolls must be secured by chocks or other means to prevent movement when stored horizontally.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-29037, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-29037, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-300
Machine room equipment and procedures.
(1) Pulp and paper machines must be equipped with emergency stopping control(s) which can be actuated quickly from all normal operating stations. If useful for the safety of personnel, the stopping control(s) must be interlocked with adequate retarding or braking action to stop the machine as quickly as is practical. The devices must consist of push buttons for electric motive power (or electrically operated engine stops), pull cords connected directly to the prime mover, control clutches, or other devices.
(2) Steps and footwalks along the fourdrinier/forming and press section must have nonslip surfacing and be complete with standard handrails, when practical.
(3) If a machine must be lubricated while in operation an automatic lubricating device must be provided or oil cups and grease fittings must be provided which can be serviced safely without exposing the worker to any hazards.
(4) All levers carrying weights must be so constructed that weights will not slip or fall off.
(5) Guarding inrunning nip points. The drums on pulp and paper machine winders must be provided with suitable guards to prevent a person from being caught between the roll and the front drum on the winder when the pinch point is on the operator's side.
(a) Such guards must be interlocked with the drive mechanism to prevent the winder from running while the guard is not in place. Except that the winder may be wired to allow it to run at thread or jog speed only for adjustment and start up purposes while the guard is not in position.
(b) A zero speed switch or locking device must be installed to prevent the guard from being removed while the roll is turning above thread or jog speed.
(c) Rewinders.
When rewinding large rolls and the nip point is adjacent to the normal work area:
(i) The nip point must be protected by a barrier guard;
(ii) Such guard must be interlocked with the drive mechanism to prevent operating the machine above thread or jog speed without the guard in place; and
(iii) A zero speed switch must be installed to prevent the guard from being raised while the roll is turning.
(d) Inrunning nips where paper is not being fed into a calender must be guarded.
(6) An audible alarm must be sounded prior to starting up any section of a pulp or paper machine. Sufficient time must be allowed between activation of the alarm system and start up of the equipment to allow any persons to clear the hazardous area.
(7) When starting up a dryer section, steam to heat the drums must be introduced slowly and while the drums are revolving.
(8) A safe method must be used when starting paper into the nip of drum type reels or calender stacks. This may be accomplished by the use of feeder belts, carrier ropes, air carriage or other device or instrument.
(a) A rope carrying system should be used wherever possible at points of transfer; or
(b) Sheaves should be spaced so that they do not create a nip point with each other and the sheave and its support should be capable of withstanding the speed and breaking strength of the rope for which they are intended.
(9) Employees must not feed a stack with any hand held device which is capable of going through the nip.
(10) Employees must not attempt to remove a broken carrier rope from a dryer while the section is running at operating speed.
(11) Employees must stop the dryer to remove a wrap except in cases where it can be safely removed by using air or other safe means.
(12) To remove deposits from rolls, a specially designed scraper or tool must be used. Scraping of rolls must be performed on the outgoing nip side.
(13) Doctor blades.
(a) Cleaning. Employees must not place their hands between the sharp edge of an unloaded doctor blade and the roll while cleaning the doctor blade.
(b) Doctor blades must have the sharp edges properly guarded during transportation and storage.
(c) Special protective gloves must be provided and must be worn by employees when filing or handling sharp edged doctor blades.
(14) Handling reels.
(a) Reels must stop rotating before being lifted away from reel frame.
(b) Crane hooks must not be used to stop a turning reel.
(c) Exposed rotating reel shafts with square block ends must be guarded.
(d) The crane operator must ascertain that reels are properly seated at winder stand or at reel arms before they disengage the hooks.
(e) On stored reels, a clearance of at least 8 inches between the reels of paper must be maintained.
(15) All winder shafts must be equipped with a winder collar guide. The winder must have a guide rail to align the shaft for easy entrance into the opened rewind shaft bearing housing. If winder shafts are too heavy for manual handling, mechanical equipment must be used.
(16) Shaftless winders must be provided with a barrier guard of sufficient strength and size to confine the rolls in the event they become dislodged while running.
(17) All calender stacks and spreader bars must be grounded according to chapter 296-24 WAC, Part L, and WAC 296-800-280 as protection against shock induced by static electricity.
(18) Nonskid type surface required.
(a) All exposed sole plates between dryers, calenders, reels, and rewinders must have a nonskid type surface.
(b) A nonskid type surface must be provided in the work areas around the winders or rewinders.
(19) If a powered roll ejector is used it should be interlocked to prevent accidental actuation until the receiving platform or roll lowering table is in position to receive the roll.
(20) Employees must keep clear of hazardous areas around the lowerator, especially all lowerator openings in a floor and where roll is being discharged.
(21) Provision must be made to hold the rider roll when in a raised position unless counterbalancing eliminates the hazard.
(22) Drain openings in pits. Flush floor drain openings larger than 3 inches in diameter in the bottom of pits must be guarded to prevent workers from stepping through, while working in this area.
(23) Employees must not enter into or climb on any paper machine roll that is subject to free turning unless a positive locking device has been installed to prevent the roll from turning.
(24) You must ensure sufficient inspection and nondestructive examination of reel spool and calender roll journals. The type and frequency of testing must be adequate to detect indications of failure. Any reel spool or calender roll journal found to have an indication of failure must be removed from service. Nondestructive examination personnel must be qualified in accordance with SNT-TC 1A.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-300, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040, and [49.17].050. WSR 01-11-038, § 296-79-300, filed 5/9/01, effective 9/1/01; WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-300, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99. Statutory Authority: Chapter 49.17 RCW. WSR 91-24-017 (Order 91-07), § 296-79-300, filed 11/22/91, effective 12/24/91. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.040, 49.17.240, and chapters 43.22 and 42.30 RCW. WSR 81-03-007 (Order 80-31), § 296-79-300, filed 1/8/81; Order 76-7, § 296-79-300, filed 3/1/76; Order 74-24, § 296-79-300, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-300, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-310
Converting operations (bag and container manufacturing, printing, coating, finishing and related processes).
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-310, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-310, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-310, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]
PDF296-79-31001
General requirements for converting operations (bag and container manufacturing, printing, coating, finishing and related processes).
(1) Guillotine-type trimmers must be designed in a manner which will require the operator to use both hands simultaneously to activate the cutting blade. If machine helpers are employed in the control function of the cutter, separate two-hand controls must be provided for the control function performed by the helper.
(2) Guillotine-type trimmers must be designed in a manner that the trimming blade will not repeat unless manually reactivated.
(3) Sorting and counting tables must be smooth and free from splinters, with edges and corners rounded.
Paddles must be smooth and free from splinters.
(4) Devices (i.e., mirrors) must be installed to assist the converting machine operator in viewing blind work stations where a hazard exists.
(5) Mechanical lifting devices must be provided for placing and removing rolls from rewinders. Rolls must not be left suspended overhead while the controls are unattended.
(6) When using a crane or hoist to place rolls into a backstand and the operator cannot see both ends of the backstand, assistance will be provided or appropriate devices will be installed to eliminate the hazards involved. The operator must ascertain that rolls are properly seated at winder stand or at roll arms before disengaging the hooks.
(7) Slitters, slotters, and scorers not in use must be properly stored so a hazard is not created.
(8) All power closing sections must be equipped with an audible warning system which will be activated when closing the sections.
(9) Roll-type embosser. The nipping point located on the operator's side must be guarded by either automatic or manually operated barrier guards interlocked with the drive.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-31001, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 76-7, § 296-79-31001, filed 3/1/76; Order 74-24, § 296-79-31001, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-31003
Corrugator.
(1) Every recessed floor conveyor system must be identified by standard color coding, and so designed and installed to minimize tripping hazards.
(2) All areas subject to wet processes must be provided with drains.
(a) Drain trenches must be provided with gratings flush with the adjoining floor.
(b) Use of curbing in work areas should be avoided in new installations. If the use of curbing cannot be avoided, the design must be such that the curbs do not constitute a tripping hazard in normal working areas. When curbing exists and constitutes a hazard, it must be color coded.
(3) Rails of rail mounted devices such as roll stands must be flush with the adjacent floor, and so installed to provide a minimum of 18 inches clearance between the equipment and walls or other fixed objects.
(4) All corrugating and pressure rolls must be equipped with appropriately designed and installed threading guides so as to prevent contact with the infeed nip of the various rolls by the operator.
(5) A minimum of 4 inches clearance or effective nip guarding must be maintained between heated drums, idler rolls, and cross shafting on all preheaters and preconditioners.
(6) Lower elevating conveyor belt rolls on the single facer bridge must have a minimum nip clearance of 4 inches or effective nip guarding.
(7) Web shears at the discharge end of the double facer must be equipped with barrier type guards.
(8) Slitter stations not in use must be disconnected from the power source by positive means.
(9) Elevating type conveyors must have the floor area color-coded.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-31003, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-31003, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-31003, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-31009
Die cutting.
Bobst type die cutters.
A minimum of 4 inches must be provided between the end of the slat and the guide bar.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-31009, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-31009, filed 5/6/74.]
PDF296-79-320
Sulfite recovery furnace area requirements.
(1) You must have a program to train all personnel associated with recovery boiler operations in safe operating procedures and emergency shutdown procedures.
(2) An audible warning system must be installed in kraft and soda base sulfite recovery furnace areas and must be actuated whenever an emergency exists.
(3) All personnel who enter the recovery furnace area must understand the emergency evacuation procedure.
(4) Warning system maintenance. Emergency warning systems in the recovery furnace areas must be kept in proper working condition and must be tested or checked weekly.
(5) Personnel must stand to the side while opening a furnace or boiler firebox door.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 17-16-132, § 296-79-320, filed 8/1/17, effective 9/1/17. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, [49.17].040 and [49.17].050. WSR 99-16-083, § 296-79-320, filed 8/3/99, effective 11/3/99; Order 74-24, § 296-79-320, filed 5/6/74; Order 70-6, § 296-79-320, filed 7/10/70, effective 8/10/70.]