PDFWAC 296-32-210
Definitions.
The terms used in these standards will be interpreted in the most commonly accepted sense consistent with the communications industry. The words "shall" and "must," are used to indicate the provisions which are mandatory.
Acceptable conditions for access. The conditions that must exist before the employer authorizes and grants permission for construction, alteration, repair or maintenance work. These conditions include the following:
(a) Work under the control of a work safety program meeting the requirements of the rules in this chapter;
(b) Notwithstanding the prohibitions outlined in this rule, if emergency maintenance work must be performed where there is an accumulation of snow, ice or other slippery material, the employer must implement safe work practices (equipment, practices and procedures) that address the hazards known to be associated with work to minimize the associated risk to employees while working.
Accessible radiation. Laser radiation to which human access is possible.
Adverse weather. Does not abdicate the responsibility of the employer to provide for a safe work environment. Proper clothing and safety equipment must be suitable for the work intended. When adverse weather (such as high winds, heat, cold, lightning, rain, snow or sleet) creates a hazardous condition, operations must be suspended until the hazardous condition no longer exists.
Aerial lifts. Includes, but are not limited to, the following types of vehicle-mounted aerial devices used to elevate personnel to job sites above ground:
(a) Extensible boom platforms;
(b) Aerial ladders;
(c) Articulating boom platforms;
(d) Vertical towers;
(e) A combination of any of the above defined in ANSI A92.2-2015. These devices are made of metal, wood, fiberglass, reinforced plastic (FRP), or other material; are powered or manually operated and are deemed to be aerial lifts whether or not they are capable of rotating above a substantially vertical axis.
Aerial splicing platform. This usually or commonly consists of a platform, approximately 3 feet x 4 feet, used to perform aerial cable work. It is furnished with fiber or synthetic ropes for supporting the platform from aerial strand, detachable guy ropes for anchoring it, and a device for raising and lowering it with a handline.
Aerial tent. A small tent usually constructed of vinyl coated canvas which is usually supported by light metal or plastic tubing. It is designed to protect employees in inclement weather while working on ladders, aerial splicing platforms, or aerial devices.
Anchorage. A secure connecting point or a terminating component of a fall protection system or rescue system capable of safely supporting the impact forces applied by a fall protection system or anchorage subsystem.
Anti-two block device. A positive acting device that prevents contact between the load block or overhaul ball and the top block (two-blocking) or a system that deactivates the hoisting action before damage occurs in the event of a two-block situation.
Articulating boom lift/crane. A crane or boom lift whose boom consists of a series of folding, pin connected structural numbers, typically manipulated to extend or retract by power from hydraulic cylinders.
Assisted rescue. A rescue requiring the assistance of others.
Automatic descent control device. A load lowering device or mechanism that automatically controls pay-out speed of line or descent speed under load once it has been engaged.
Barricade. A physical obstruction such as tapes, cones, or "A" frame type wood and/or metal structure intended to warn and limit access to a work area.
Barrier. A physical obstruction which is intended to prevent contact with energized lines or equipment, or to prevent unauthorized access to a work area.
Boatswain chair. A single-point adjustable suspension scaffold consisting of a seat or sling (which may be incorporated into a full body harness) designed to support one employee in a sitting position.
Bond. An electrical connection from one conductive element to another for the purpose of minimizing potential differences or providing suitable conductivity for fault current or for mitigation of leakage current and electrolytic action.
Brakes. A mechanical or hydraulic system that can decelerate or stop a load.
Cable. An insulated or uninsulated electrical conductor, often in strands or any combination of electrical conductors that may be insulated from one another.
Cable sheath. A protective covering applied to cables.
Note: | A cable sheath may consist of multiple layers of which one or more is conductive. |
Cage. A barrier, which may be referred to as a cage guard or basket guard, that is an enclosure mounted on the side rails of the fixed ladder or fastened to the structure to enclose the climbing space of the ladder.
Capstans. A spool-shaped mechanical device mounted on the end of a shaft around which a rope is wrapped; sometimes called a cathead when used in a horizontal position; can be pole mounted, tower mounted, or truck mounted.
Carabiner. A connector generally comprised of a trapezoidal or oval shaped body with a closed gate or similar arrangement that may be opened to attach another object and, when released, automatically closes to retain the object.
Carrier. The track of a ladder safety device consisting of a flexible cable or rigid rail.
Circuit. A conductor or system of conductors through which an electric current is intended to flow; or an electrical device that provides a path for an electrical current to flow.
Clearance. The distance from a specified reference point or protection by the use of protective devices to prevent accidental contact by persons or objects on approach to a point of danger.
Climber attachment anchorage. An anchorage point for attaching a lanyard or similar fall protection device. See also "anchorage."
Climbing facilities. A series of attachments installed on a support structure, or antenna, on which a climber may step while ascending or descending, and which may incorporate or employ:
(a) Steps, rungs, cleats and/or structural members which form an integral part of the structure;
(b) Rungs, cleats or step bolts which are attached to the structure;
(c) Fixed ladders, safety devices, platforms and cages used for climbing or working on communication structures; or
(d) Climber attachment anchorages.
Climbing space. The space reserved on poles or structures that permits ready access for workers to gain access to equipment and conductors located on poles or structures.
Communication lines. The conductors and their supporting or containing structures for telephone, telegraph, railroad signal, data, clock, fire, police-alarm, community television, fiber optic, and other systems which are used for public or private signal or communication services, and which operate at potentials not exceeding 400 volts to ground or 750 volts between any two points of the circuit, and the transmitted power of which does not exceed 150 watts. When communications lines operate at less than 150 volts to ground, no limit is placed on the capacity of the system. Specifically designed communications cables may include communication circuits not complying with the preceding limitations, where such circuits are also used incidentally to supply power to communication equipment.
Communication plant. The lines and conductors and their associated equipment required to provide public or private signals for communicative service.
Communication tower. Any structure that is used primarily as an antenna or to provide attachment points for one or more antennas or signaling devices. Where the communication tower is affixed to another structure, such as an electrical transmission tower, church steeple, building rooftop, or water tower, the applicable part of any controlling regulation for protection of employees must apply up to the point of access to the communication tower.
Competent climber. An individual with the physical capabilities to climb; has actual tower climbing experience; is trained in fall protection regulations including the equipment that applies to tower work; is capable of identifying existing and potential fall hazards; and has the employer's authority to take prompt corrective action to eliminate those hazards.
Competent person. A person who has been trained pertaining to their job assignment and can identify existing and predictable hazards in their surroundings that are either unsanitary, hazardous, or dangerous to employees and has the authority by the nature of their position to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate them. The person must also be knowledgeable in the requirements of this chapter to be competent.
Competent rescuer. An individual designated by the employer who by training, knowledge and experience is capable of the implementation, supervision and monitoring of a rescue at height in the event of an emergency. This person must have the employer's authority to write the individual site rescue plan, and may be designated to manage the employer's fall protection rescue program.
Competent rigger. A person knowledgeable and experienced with the procedures and equipment common to the communication structures industry and trained to identify hazards with authorization to take prompt corrective measures.
Conductor. A material, usually in the form of a wire, cable, or bus bar, suitable for carrying an electric current.
Construction work. Includes all or any part of excavation, construction, erection, alteration, repair, demolition, and dismantling, of buildings and other structures and all operations in connection therewith; the excavation, construction, alteration and repair of sewers, trenches, caissons, conduits, pipe lines, roads and all operations pertaining thereto; the moving of buildings and other structures, and to the construction, alteration, repair, or removal of wharfs, docks, bridges, culverts, trestles, piers, abutments or any other construction, alteration, repair or removal work related thereto.
Construction work. For purposes of Part C of this chapter also means field activities related to the installation, alteration, maintenance or demolition/decommission of antenna supporting structures and antennas.
Contract employer. An employer, other than a host employer, that performs work covered by this chapter under contract.
Crew. A group of two or more employees of one employer sent to a worksite to work on the same project.
Crew chief/supervisor/foreman. One who is authorized and designated as competent and qualified by the employer.
Crewleader or person-in-charge. Person directly in charge of employees doing the work regardless of title.
Crown block (top block). The upper sheave assembly attached to a structure used to change the direction of a load or jump line coming from a hoist.
Deceleration distance. The vertical distance between the user's fall arrest attachment at the onset of fall arrest forces during a fall, and after the fall arrest attachment comes to a complete stop.
Direct communications. The effective and reliable two-way communication, being able to send and receive communications, between crew members or crews using normal voice communication, visual, radio, or cellular means.
Effectively grounded. Intentionally connecting equipment to earth through a ground connection or connections of sufficiently low impedance and having sufficient current-carrying capacity to prevent the transmission of fault current or voltages which may result in undue hazard to employees or connected equipment.
Elevated (high angle) rescue. The process by which emergency methods and equipment are utilized in order to gain access to and egress from the location of an injured employee(s) on a tower structure, or other elevated structures and lower both the injured employee(s) and the rescuer(s) to the ground safely.
Emergency. An unforeseen occurrence endangering life, limb, or property which requires immediate action.
Emergency washing facilities. Typically consist of emergency showers, eyewashes, eye/face washes, hand-held drench hoses, or other similar units.
Energized(alive or live). Electrically connected to a source of potential difference or electrically charged so as to have a potential different from that of the earth or different from that of adjacent conductors or equipment.
Engineer of record (EOR). A registered professional engineer with expertise in the discipline applicable to the scope of work and responsible for the structural adequacy of the design of the structure in the completed project.
Engineered hoist system. A hoist system that is the complete system for hoisting, including: The frame, mounts and/or anchorages, prime mover (winch assembly), motors, drums, truck chassis (if used as the base for the hoist), wheel chocks, wire rope, hour meter, foot blocks, gin pole (if used), and rooster head or cat head, as applicable.
Equipment. A general term which includes materials, fittings, devices, appliances, fixtures, apparatus, and similar items used as part of, or in connection with, a supply or communications installation; to include all machinery used in the performance of constructing and maintaining communication systems.
Exit. Provides a way of travel out of the workplace.
Exit route. A continuous and unobstructed path of exit or travel from any point within a communications workplace, structure, or site to provide a safe means of withdrawal.
Exposed live parts. Electrical parts that are not suitably covered, guarded, isolated, or insulated and are capable of being accidentally accessed, touched or approached closer than a safe distance.
Exposed wiring methods. Those methods working with electrical wires that are attached to surfaces or behind panels designed to allow access to the wires.
Fall arrest. The action or event of stopping a free fall or the instant where the downward free fall has been stopped.
Fall arrest system. The collection of equipment components that are configured to arrest a free fall.
Fall protection equipment. The personal equipment that employees utilize in conjunction with fall protection systems, including connectors, body belts or body harnesses, lanyards, ropes, deceleration devices, and anchorage points to ensure 100 percent fall protection for the employees.
Fall protection work plan. A written planning document in which the employer identifies all areas on the job site where fall hazards may exist. Detailed requirements relating to a fall protection work plan are covered in WAC 296-32-22555 and 296-32-24012 of this chapter.
Fall restraint. A system in which all necessary components function together to restrain or prevent an employee from falling to a lower level. Types of fall restraint systems include guardrail systems and personal fall restraint system(s) that prevents the user from falling any distance. The system is comprised of either a lineman's belt or full body harness, along with an anchorage, connectors and other necessary equipment. The other components typically include a lanyard, and may also include a lifeline and other devices.
Fiber-optic cable - Communication. A fiber-optic cable meeting the requirements for a communication line and located in the communication space of overhead or underground facilities.
Fiber-optic cable - Supply. A fiber-optic cable located in the supply space of overhead or underground facilities.
Field work. The construction, installation, operation, maintenance, rearrangement, and removal of conductors, antenna systems, and other equipment used for signal or communication service, and of their supporting or containing structures for landline or wireless communications.
First aid. The extent of treatment you would expect from a person trained in basic first aid, using supplies from a first-aid kit. Tests, such as X-rays, must not be confused with treatment.
Flemish eyes (Molly Hogan). An eye splice made by using stranded cable and weaving them together to make an eye.
Floor hole. An opening measuring less than twelve inches but more than one inch in its least dimension in any floor, roof, platform, or surface through which materials but not persons may fall, such as a belt hole, pipe opening, or slot opening.
Floor opening. An opening measuring twelve inches or more in its least dimension in any floor, roof, platform, or surface through which persons may fall.
Foot block (heel or base block). A block stationed or positioned at the base of a structure or pole that allows a line, rope or wire rope to change direction 90 degrees to go up the structure.
Full body harness. A body support that is designed to contain the torso in such a manner that fall arrest forces are distributed over at least the upper thighs, pelvis, chest, and shoulders, with provisions for attaching a lanyard, lifeline, or deceleration devices. These specifications must meet the requirements specified in ANSI Z359.1-2007.
Gin pole. A device unique to the telecommunications industry and is used to raise successive sections of tower steel, antennas, personnel or equipment into position. This temporary device allows headroom above the highest fixed point of the tower or structure.
Gross load. The total load to be lifted. This includes the weight of the lifted object, headache ball, the load line, tag line, and any other attachments.
Ground. A conductive body, usually earth, to which an electric potential is referenced; the connecting or establishment of a connection, whether by intention or by accident; a conducting connection, between an electric circuit and equipment and earth or to some other conducting body that serves in place of the earth.
Grounded. To be positively connected to or in contact with earth or connected to an extended conduction body that serves instead of earth. A conducting object such as, but not limited to, a wire that is connected to such a position as zero potential. A connection has been made between an electrical circuit or equipment and the earth or another conducting body besides the earth, used as an arbitrary zero of potential.
Grounding(for employee protection). The act of placing shorts and grounds on conductors and equipment for the purpose of protecting employees from dangerous voltages while working on such lines or equipment.
Ground tent. A small tent usually constructed of vinyl coated canvas supported by a metal or plastic frame. Its purpose is to protect employees and the equipment from inclement weather while working at buried cable pedestal sites or similar locations.
Grounded conductor. A system or circuit conductor which is intentionally grounded.
Grounded systems. A system of conductors/equipment in which at least one conductor or point is intentionally grounded, either solidly or through a current-limiting device (not a current-interrupting device).
Grounding electrode conductor (grounding conductor). A conductor used to connect equipment or the grounded components of a wiring system to a grounding electrode.
Guard or guarded. Covered, shielded, fenced, enclosed, or otherwise protected by means of suitable covers, casings, barriers, rails, screens, mats, platforms, or warning signs or devices to remove the possibility of dangerous contact to lines, equipment or devices, limiting or preventing approach by other persons or objects to a point of danger.
Guardrails. A type of fall restraint system that is a horizontal barrier consisting of a top rail and mid rail, and toe board when used as falling object protection for persons who may work or pass below, that is erected along all open sides or edges of a walking/working surface, a floor opening, a floor hole, wall opening, ramp, platform, or runway.
Handrail. A single bar or pipe supported on brackets from a wall or partition to provide a continuous handhold for persons using a stair.
Hazard. Any condition, potential or inherent, which can cause injury, death, or occupational disease.
High wind. A wind condition that is determined to be at such velocity as to create a hazard to the employees performing aerial tasks as an employee would be exposed to being blown from elevated locations, lose footing and control; that wind speed which has been determined to be unsafe by the manufacturer of the particular equipment being used (cranes, lifts, booms, etc.) and/or equipment being installed. Winds exceeding 25-30 miles per hour (48.3 kilometers per hour) if material handling is involved, winds exceeding 40 miles per hour (64.4 kilometers per hour) are normally considered as meeting this criteria.
Hoist mechanism or hoist. The complete unit including frame, prime mover (winch assembly), pumps, motors, drums, and any associated equipment that is necessary to make the complete unit work and is used to lift a load.
Hoisting. The act of lifting and/or lowering loads or personnel.
Horizontal lifeline. A rail, rope, wire, or synthetic cable that is installed in a horizontal plane between two anchorages and used for attachment of an employee's lanyard or lifeline device while moving horizontally.
Host employer. An employer who operates or maintains telecommunications facilities covered by this chapter and who authorizes a contract employer to perform work on that installation.
Note to the definition of "host employer": | |
The Division of Safety and Health (DOSH) will treat the telecommunication company or the owner of the installation as the host employer if it operates or controls operating procedures for the installation. If the telecommunication company or installation owner neither operates nor controls operating procedures for the installation, DOSH will treat the employer that the telecommunication owner has contracted with to operate or control the operating procedures for the installation as the host employer. In no case will there be more than one host employer. | |
Individual-rung/step ladder. A fixed ladder consisting of individual steps, rungs or climbing pegs mounted directly to the surface, side or wall of the pole, structure, building, equipment, or vault.
Insulated. Separated from other conducting surfaces by a dielectric substance for the intended applied voltage or may be subject to (including air space) offering a high resistance to the passage of current.
Note: | When any object is said to be insulated, it is understood to be insulated in suitable manner for the conditions to which it is subjected. Otherwise, it is, within the purpose of these standards, uninsulated. Insulating coverings of conductors is one means of making the conductor insulated. |
Insulation (as applied to cable). That which is relied upon to insulate the conductor from other conductors or conducting parts or from ground.
Job hazard assessment. A process used to identify hazards and the methods to eliminate or control those hazards.
Joint use. The sharing of a common facility, such as a manhole, trench or pole, by two or more entities or utilities such as, but not limited to, power, alarm systems, signal lighting and telecommunications.
Ladder. A device incorporating or employing steps, rungs, or cleats.
Ladder platform. A device designed to facilitate working aloft from an extension ladder. A typical device consists of a platform (approximately 9" x 18") hinged to a welded pipe frame. The rear edge of the platform and the bottom crossmember of the frame are equipped with latches to lock the platform to ladder rungs.
Ladder safety device. Any device, other than a cage or well, designed to arrest the fall of a person using a fixed ladder.
Ladder safety system. A system designed to eliminate or reduce the possibility of falling from a ladder. A ladder safety system usually consists of a carrier, safety sleeve, lanyard, connectors, and body harness. Cages and wells are not ladder safety systems.
Ladder seat. A removable seat used to facilitate work at an elevated position on rolling ladders in telecommunication centers.
Landing. An area such as the ground, roof, or platform that provides access/egress for a fixed ladder.
Laser safety officer. One who has authority and responsibility to monitor and enforce the control of laser hazards and effect the knowledgeable evaluation and control of lasers.
Length of climb. The total vertical distance a person could climb in traveling between the extreme points of access/egress for a fixed ladder, whether the ladder is of an unbroken length or consists of multiple sections. This total vertical distance is determined by including all spaces between all ladder steps or rungs and all other vertical intervening spaces between the extreme points of access/egress.
Line clearance tree trimming. The pruning, trimming, repairing, maintaining, removing or clearing of trees or the cutting of brush that is within 10 feet (305 cm) of electric supply lines or equipment.
Lineman's body belt. A body support comprised of a strap, at least four inches in width, designed to be compatible with an approved fall restraint system.
Line patrol. Looking at aerial plants after storm damage for damaged lines.
Line truck. A truck used to transport employees, tools, and material, and to serve as a traveling workshop for telecommunication installation and maintenance work. It is sometimes equipped with a boom and auxiliary equipment for setting poles, digging holes, and elevating material or employees.
Listed. Equipment that is listed in a publication by a nationally recognized laboratory (such as, but not limited to, UL (Underwriters' Laboratories, Inc.)) that inspects and approves that type of equipment. Listed equipment must also state that the equipment meets nationally recognized standards or has been tested and found safe to use in a specific manner.
Load chart. A chart used that is affixed to and specific to the equipment to determine the lifting capacities under specified parameters and an understanding of the working parameters within which the capacities are to be used.
Load line. A synthetic or wire rope of sufficient size, durability and strength to raise and lower the intended gross load safely.
Locking snap hook. A connecting snap hook that requires two separate forces to open the gate; one to deactivate the gatekeeper and a second to depress and open the gate which automatically closes when released; used to minimize roll out or accidental disengagement.
Lockout. Placing a lockout device on an energy-isolating device using an established procedure to make sure the machine or equipment cannot be operated until the lockout device is removed.
Lockout device. A device that uses a positive means, such as a key or combination lock, to hold an energy-isolating device in the "safe" or "off" position. This includes blank flanges and bolted slip blinds.
Manhole. A subsurface enclosure which personnel may enter and which is used for the purpose of installing, operating, and maintaining underground and submersible equipment and/or cable.
Manhole platform. A platform consisting of separate planks which are laid across platform supports. The ends of the supports are engaged in the manhole cable racks or approved support points designed for human support.
Manlift equipment. Types of portable truck-, trailer-, crane-mounted equipment, such as mechanical, electric or hydraulic ladders and boom-mounted or suspended buckets, platforms or cages.
Manual descent control device with automatic lockoff. A manual descent control device with automatic lockoff features having provision for both "hands-free" and "panic" locking capabilities.
Maximum intended personnel load/gross load. The total load and weight of all employees; their tools, materials, load lines, and other loads reasonably anticipated to be applied to the hoist apparatus when an employee is hoisted.
Maximum permissible exposure (MPE). The rms and peak electric and magnetic field strength, their squares, or the plane-wave equivalent power densities associated with these fields to which a person may be exposed without harmful effect and with an acceptable safety factor.
May (and "should") or "it is recommended" are used to indicate the provisions are not mandatory but are recommended.
Microwave transmission. The act of communicating, sending, receiving or signaling utilizing a frequency between 1 GHz (gigahertz) and 300 GHz inclusively.
Mobile crew. A work crew that routinely moves to a different work location periodically. Normally a mobile crew is not at the same location all day.
Multi-use site for towers and antennas. Any site where more than one subscriber has antennas for the use of communication purposes.
Must (and "shall") as used in this chapter make the provisions mandatory.
Nearby facility. A sanitary facility that is within three minutes travel by the transportation provided.
NEMA. These initials stand for National Electrical Manufacturing Association.
Nominal voltage. The nominal voltage of a system or circuit is the value assigned to a system or circuit of a given voltage class for the purpose of convenient designation. The actual voltage may vary above or below this value.
Nonionizing radiation (RFR) as related to industrial sources. Electromagnetic radiation within the spectral range of approximately 200 nanometers to 3 kilometers including ultraviolet, visible, infrared and radiofrequency/microwave radiation.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Figure 1
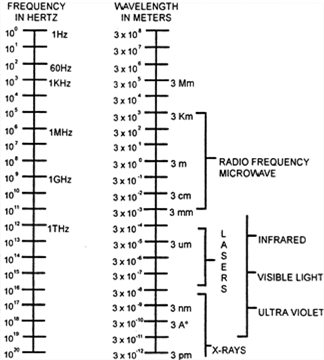 |
Normally unattended work location. An unattended site that is visited occasionally by one or more employees.
Oil sample analysis. A method used to evaluate oil, which may not necessarily mean a laboratory analysis, but one that could be effectively accomplished in the field by a qualified person; usually done to evaluate/ascertain the PCB levels or insolative qualities of the oil.
One hundred percent (100 percent) fall protection. Each employee exposed to fall hazards above 4 feet while ascending or descending, moving point to point, or working from a platform, crane basket, lift or bucket truck; must be protected by fall protection 100 percent of the time.
Operator (equipment). A person who runs or operates equipment used in the construction and maintenance of communication systems.
Permissible exposure limits (PELs). A time-weighted average (TWA) of exposure for an eight-hour work day within a forty-hour workweek. Exceptions are those limits which are given a ceiling value.
Personal eyewash units. Portable, supplementary units that support plumbed units or self-contained units, or both, by delivering immediate flushing for less than fifteen minutes.
Platform. A work surface elevated above the surrounding floor or ground level.
Pole balcony or seat. A balcony or seat used as a support for employees at pole-mounted equipment or terminal boxes. A typical device consists of a bolted assembly of composite or steel details and a wooden platform. Composite or steel braces run from the pole to the underside of the balcony.
Pole platform. A platform intended for use by an employee in splicing and maintenance operations in an elevated position adjacent to a pole. It consists of a platform equipped at one end with a hinged chain binder for securing the platform to a pole. A brace from the pole to the underside of the platform is also provided.
Portable ladder. A ladder that can be readily moved or carried.
Positioning system. A body belt or full body harness system configured to allow an employee to be supported on an elevated vertical or inclined surface, such as a wall, and work with both hands free from body support.
Positive locking system. A system that creates a mechanical means of ensuring that the connection or interface between two components will not slip.
Potable water. Water that you can safely drink that meets specific safety standards prescribed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency's National Interim Primary Drinking Water Regulations, published in 40 C.F.R. Part 141 and 40 C.F.R. 147.2400.
Powered lowering. The act of controlled lowering of a load by the use of a system or device in the power train, which can control the lowering speed of the winch assembly.
Prime mover. The system that provides the energy to rotate the winch assembly.
Proficient. A thorough competence derived from training and practice.
Proof test. The act of testing the rigging and hoist mechanism whenever newly rigged or after any changes are made to the hoist mechanism or rigging.
Protection from hazardous voltage. The isolation from or deenergizing of equipment to prevent accidental contact by persons or objects on approach to point of danger.
Protective devices or equipment. Those devices such as rubber gloves, rubber boots, rubber blankets, line hose, rubber hoods or other insulating devices or equipment, which are specially designed and appropriate for the electrical protection of employees.
Public highway. Every way, land, road, street, boulevard, and every way or place in the state open as matter of right to public vehicular travel, both inside and outside the limit of cities and towns.
Pulley. A sheave wheel that is grooved on the outer circumference to hold a wire or synthetic rope in place while turning and allows a mechanical advantage for lifting or a change in direction.
Qualified engineer. A professional engineer knowledgeable and experienced in engineering related practices for communication structures and/or lifting systems and rigging components commonly used in the communication industry.
Qualified line-clearance tree trimmer. A tree worker who through related training and on-the-job experience is familiar with the special techniques and hazards involved in line clearance.
Qualified line-clearance tree trimmer trainee. Any employee regularly assigned to a line-clearance tree-trimming crew and undergoing on-the-job training who, in the course of such training, has demonstrated their ability to perform duties safely at their level of training.
Qualified person. One who is familiar with the construction, maintenance, and operation of the equipment and hazards involved, or who has passed a journeyman's examination for the particular branch of the trades with which they may be connected, and trained in the methods necessary to identify and eliminate those hazards. An employee considered to be a qualified person depends on various circumstances in the workplace and on the level of training they have received and demonstrated competency with the tasks required of the job.
Radio frequency radiation (RFR). See nonionizing radiation.
Rated capacity. The load that a winch assembly may handle under given operating conditions and at a known design factor.
Record. Any item, documentation, collection, or grouping of information.
Registered professional engineer (RPE). A registered professional engineer licensed under RCW 18.43.040(1).
Remote site/worksite. A site/worksite that is over thirty minutes from emergency medical services or does not have reliable communications.
Rescue. The process of removing a person from danger, harm, or confinement to a safe location.
Rescue plan. A written process that describes in a general manner how rescue is to be approached under the specified parameters, such as location or circumstances.
Rescue procedure. A written series of logical steps that describes the specific manner in which rescue is to be accomplished.
Rescue system. An assembly of components and subsystems used for rescue.
Rescue system, one person. A rescue system intended to bear only the weight of a single person at one time.
Rescue system, two persons. A rescue system intended to bear the weight of up to two persons simultaneously.
Retraining. Classroom and/or on-the-job instruction required for continued retention of previously learned materials or skills.
Rigging. Includes, but is not limited to, chains, slings, ropes, pulleys, hooks, and all accompanying hardware for lifting, lowering, suspending, and fastening loads.
Rigging plan. A systematic and detailed presentation showing the equipment and procedures required for a construction process that will provide for the safety of personnel and for the stability of the structure and lifted components.
Rise. The vertical distance from the top of a tread to the top of the next higher tread.
Riser. The vertical part of the step at the back of a tread that rises to the front of the tread above.
Rooster head. A sheave assembly located at the top of a gin pole capable of rotating 360 degrees or fixed that allows a load line to pass through and return to a vertical position.
Rung. A ladder crosspiece used in climbing or descending. Also called a cleat or step.
Safety climb system. An assembly of components whose function is to arrest the fall of a user, including the carrier and its associated attachment elements (e.g., brackets, fasteners), the safety sleeve, and the body support and connectors, wherein the carrier is permanently attached to the climbing face of the ladder or immediately adjacent to the structure.
Safety sleeve. The part of a ladder safety system consisting of the moving component with locking mechanism that travels on the carrier and makes the connection between the carrier and the full body harness.
Safety watch system. A fall protection system as described in WAC 296-32-22555(10), in which a competent person monitors one worker who is engaged in repair work or servicing equipment on low pitch roofs only.
Self-retracting lanyard (SRL). A self-retracting device suitable for applications in which the device is mounted or anchored so a possible free fall is limited to 2 feet (.6 m) or less.
Shall (and "must") as used in this chapter make the provisions mandatory.
Sheath. Applied to sharp tools that effectively covers the tool.
Should (and "may") or "it is recommended" are used to indicate the provisions are not mandatory but are recommended.
Side plates. The side plates of sheaves or double plate attachment points that support the sheave.
Side-step ladder. A rail ladder that requires stepping from the ladder in order to reach a landing.
Similar structures. Any structure that holds equipment relevant to the communication industry.
Single ladder. A nonself-supporting portable ladder, nonadjustable in length, consisting of one section. The size is designated by the overall length of the side rail.
Site/worksite. Any location where communications work is performed or equipment is located to include communications tower or antenna and the surrounding land or property where the tower or antenna work is being performed.
Slings. An assembly to be used for lifting when connected to a lifting mechanism. The upper portion of the sling is connected to the lifting mechanism and the lower support the load, such as looped wire rope, synthetic strap, or chain for supporting, cradling, or lifting an object.
Special-purpose ladder. A portable ladder that is made by modifying or combining design or construction features of the general-purpose types of ladders in order to adapt the ladder to special or specific uses.
Special tools and equipment. Includes, but is not limited to, high voltage detector and RFR monitor.
Specular reflection. A mirror-like reflection.
Stair railing. A vertical barrier attached to a stairway with an open side to prevent falls. The top surface of the stair railing is used as a handrail.
Stairs or stairway. A series of steps and landings that lead from: One level or floor to another; to platforms, pits, boiler rooms, crossovers, or around machinery, tanks, and other equipment; and are used more or less continuously or routinely by employees, or only occasionally by specific individuals. A stair or stairway may also be defined as having three or more risers.
Standard safeguard. Safety devices that prevent hazards by their attachment to machinery, appliances, tools, buildings, and equipment. These safeguards must be constructed of metal, wood, or other suitable materials. The department makes the final determination about whether a safeguard is sufficient for its use.
Static brakes. Brakes used once the motion of the drum has come to a complete stop to prevent creeping or slippage. Static brakes are not necessarily separate from the primary braking system or may be redundant in application. A locking device on a primary braking system may be used.
Step. A ladder crosspiece used in climbing or descending. Also called a cleat or rung.
Step bolt. A round or flat member affixed to the structure on one end with the other end having a means to prevent the foot from sliding off.
Strand. A stranded wire used to support a conductor, pole or other structures, such as "guys," etc.
Structure owner. The employer responsible for controlling, operating and maintaining the structure.
Subcontractor. The employer engaged by the owner or general contractor responsible for completing specific portions of a project in accordance with all applicable specifications.
System operator/owner. The person or organization that operates or controls the electrical conductors involved.
Tag line and/or trolley line. A method or system of applying a force to control a load and having the ability to create a space between the load and structure or gin pole.
Tagout. Placing a tagout device on an energy-isolating device using an established procedure to indicate that the energy-isolating device and the machine or equipment being controlled may not be operated until the tagout device is removed.
Tagout device. A prominent warning device, such as a tag and a means of attachment. It can be securely fastened to an energy-isolating device to indicate that the energy-isolating device and the machine or equipment being controlled may not be operated until the tagout device is removed.
Teardown inspection. The complete disassembly, cleaning, inspection, and replacement of all worn, cracked, corroded or distorted parts such as pins, bearings, shafts, gears, brake rotors, brake plates, drum, and base that may affect the operation of the winch assembly.
Telecommunications facility. A site or installation of communication equipment under the exclusive control of an organization providing telecommunications service, that is located outdoors or in a vault, chamber, or a building space used primarily for such installations.
Note: | Telecommunication facilities are established, equipped and arranged in accordance with engineered plans for the purpose of providing telecommunications service. They may be located on premises owned or leased by the organization providing telecommunication service, or on the premises owned or leased by others. This definition includes switch rooms (whether electromechanical, electronic, or computer controlled), terminal rooms, power rooms, repeater rooms, transmitter and receiver rooms, switchboard operating rooms, cable vaults, and miscellaneous communications equipment rooms. Simulation rooms of telecommunication facilities for training or developmental purposes are also included. |
Telecommunications digger derricks. Rotating or nonrotating derrick structures permanently mounted on vehicles for the purpose of lifting, lowering, or positioning hardware and materials used in telecommunications work.
Telecommunication service. The furnishing of a capability to signal or communicate at a distance by means such as telephone, telegraph, police and fire-alarm, community antenna television, or similar system, using wire, conventional cable, coaxial cable, wave guides, microwave transmission, or other similar means.
Through ladder. A rail ladder that requires stepping through the ladder in order to reach a landing.
TIA maintenance and condition assessment. A comprehensive assessment that addresses the following items - Structure condition, finish, lighting, grounding, antennas and lines, appurtenances, insulator condition (if applicable), guy wires condition and tensions, concrete foundations, guyed mast anchors and structure alignment (plumb). Once the assessment occurs, a maintenance plan is adopted, if not corrected during the assessment, to bring the structure within recommended TIA, manufacturer or engineer of record guidelines.
Time-weighted average (TWA). An exposure limit, averaged over eight hours that must not be exceeded during an employee's work shift.
Toeboard. A horizontal barrier at floor level erected along all open sides or edges of a floor opening, platform, runway, ramp, or other walking/working surface to prevent materials, tools, or debris from falling onto persons passing through or working in the area below.
Tower and tower site. See "site."
Tower construction. The building of a new tower or structure, or the installation of new equipment on an existing tower or structure.
Tower maintenance work. The replacement or work on any device on an existing tower, the repair of existing equipment, and painting.
Training program. A program designed to provide education through an established system of designing, developing, delivering, monitoring, evaluating, documenting and managing, safety, health and environmental training.
Tread. As used in stairs and stair railings summary (see WAC 296-800-250), the horizontal part of the stair step.
Tread run. As used in stairs and stair railings summary (see WAC 296-800-250), the distance from the front of one stair tread to the front of an adjacent tread.
Tread width. The distance from front to rear of the same tread including the nose, if used.
Trial lift. Testing a specified load weight from ground level to the location of where personnel or equipment are to be hoisted.
Two blocking. An unsafe condition that occurs on a system when the overhaul ball, hook block, or headache ball on the load line comes in contact with the main load sheave.
UL (Underwriters' Laboratories, Inc.). You will find these initials on electrical cords and equipment. The initials mean the cord or equipment meets the standards set by the Underwriters' Laboratories, Inc.
Unvented vault. An enclosed vault in which the only openings are access openings.
Vault. An enclosure above or below ground which personnel may enter, and which is used for the purpose of installing, operating, and/or maintaining equipment and/or cable which need not be of submersible design.
Vented vault. An enclosure, with provision for air changes using exhaust flue stack(s) and low level air intake(s), operating on differentials of pressure and temperature providing for air flow.
Vertical lifeline. A vertical suspended flexible line used with a fall arrestor system to arrest a fall while a worker is in the act of climbing or stationary. When following the manufacturer's specifications vertical lifelines can be used for other configurations.
Voltage communications. Voltage used for electronic communications equipment to which employees or protective equipment may be subjected.
(a) High - Over 600 volts to ground - RMS AC or DC or over 1,000 volts RMS across bare parts.
(b) Medium high - 151 to 600 volts to ground - RMS AC or DC or 301 to 1,000 volts RMS AC across any bare parts.
Voltage electric supply. The maximum effective line voltage to which the employees or protective equipment may be subjected.
(a) Low includes voltages from 100 to 600 volts.
(b) High includes voltages 601 volts and above.
Voltage of an effectively grounded circuit. The highest nominal voltage available between any conductor and ground unless otherwise indicated.
Voltage of a circuit not effectively grounded. The highest nominal voltage available between any two conductors. If one circuit is directly connected to and supplied from another circuit of higher voltage (as in the case of an autotransformer), both are considered as of the higher voltage, unless the circuit of lower voltage is effectively grounded, in which case its voltage is not determined by the circuit of higher voltage. Direct connection implies electric connection as distinguished from connection merely through electromagnetic or electrostatic induction.
Voltage, nominal. A value assigned to a circuit or system to designate its voltage class (120/240, 480Y/277, 600, etc.). The actual circuit voltage can vary from the value if it is within a range that permits the equipment to continue operating in a satisfactory manner.
Watertight. Constructed so that moisture will not enter the enclosure or container.
Weatherproof. Constructed or protected so that exposure to the weather will not interfere with successful operation. Rainproof, rain tight, or watertight equipment can fulfill the requirements for weatherproof where varying weather conditions other than wetness, such as snow, ice, dust, or temperature extremes, are not a factor.
Well. A walled enclosure around a fixed ladder that provides a person climbing the ladder with the same protection as a cage.
Winch/hoist. A mechanical device for lifting and lowering loads by winding rope onto or off a drum.
Wire rope (cable). A rope made of strands of metal wire; a cord of metal wire used to operate, suspend or pull a mechanism or winch line.
Working length. The length of a nonself-supporting ladder, measured along the rails, from the base support point of the ladder to the point of bearing at the top.
[Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, and 49.17.060. WSR 20-20-109, § 296-32-210, filed 10/6/20, effective 11/6/20. Statutory Authority: RCW 49.17.010, 49.17.040, 49.17.050, 49.17.060, and chapter 49.17 RCW. WSR 17-20-069, § 296-32-210, filed 10/2/17, effective 1/1/18. Statutory Authority: Chapter 49.17 RCW. WSR 94-15-096 (Order 94-07), § 296-32-210, filed 7/20/94, effective 9/20/94; Order 76-38, § 296-32-210, filed 12/30/76; Order 75-41, § 296-32-210, filed 12/19/75.]